Caveolin-2 is targeted to lipid droplets, a new "membrane domain" in the cell
- PMID: 11238462
- PMCID: PMC2198803
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.152.5.1079
Caveolin-2 is targeted to lipid droplets, a new "membrane domain" in the cell
Abstract
Caveolin-1 and -2 constitute a framework of caveolae in nonmuscle cells. In the present study, we showed that caveolin-2, especially its beta isoform, is targeted to the surface of lipid droplets (LD) by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy, and by subcellular fractionation. Brefeldin A treatment induced further accumulation of caveolin-2 along with caveolin-1 in LD. Analysis of mouse caveolin-2 deletion mutants revealed that the central hydrophobic domain (residues 87-119) and the NH(2)-terminal (residues 70-86) and COOH-terminal (residues 120-150) hydrophilic domains are all necessary for the localization in LD. The NH(2)- and COOH-terminal domains appeared to be related to membrane binding and exit from ER, respectively, implying that caveolin-2 is synthesized and transported to LD as a membrane protein. In conjunction with recent findings that LD contain unesterified cholesterol and raft proteins, the result implies that the LD surface may function as a membrane domain. It also suggests that LD is related to trafficking of lipid molecules mediated by caveolins.
Figures


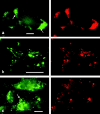

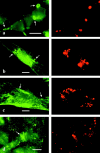



Comment in
-
Caveolin, cholesterol, and lipid droplets?J Cell Biol. 2001 Mar 5;152(5):F29-34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.5.f29. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11238468 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Accumulation of caveolin in the endoplasmic reticulum redirects the protein to lipid storage droplets.J Cell Biol. 2001 Mar 5;152(5):1071-8. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.5.1071. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11238461 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the hydrophobic domain in targeting caveolin-1 to lipid droplets.J Cell Biol. 2004 Jan 5;164(1):69-78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200303037. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14709541 Free PMC article.
-
A caveolin dominant negative mutant associates with lipid bodies and induces intracellular cholesterol imbalance.J Cell Biol. 2001 Mar 5;152(5):1057-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.152.5.1057. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11238460 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolins, caveolae, and lipid rafts in cellular transport, signaling, and disease.Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;82(1):129-44. doi: 10.1139/o03-071. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15052333 Review.
-
Caveolins: structure and function in signal transduction.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2004;9(2):195-220. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15213803 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel insights into the role of caveolin-2 in cell- and tissue-specific signaling and function.Biochem Res Int. 2011;2011:809259. doi: 10.1155/2011/809259. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Biochem Res Int. 2011. PMID: 22229094 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview on Lipid Droplets Accumulation as Novel Target for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Therapy.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 30;11(12):3186. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123186. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid droplets and cellular lipid metabolism.Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:687-714. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-061009-102430. Epub 2012 Apr 13. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22524315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovered Key CpG Sites by Analyzing DNA Methylation and Gene Expression in Breast Cancer Samples.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 1;10:815843. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.815843. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35178391 Free PMC article.
-
The skinny on fat: lipolysis and fatty acid utilization in adipocytes.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Nov;20(9):424-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.06.002. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19796963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson R.G.W. The caveolae membrane system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998;67:199–225. - PubMed
-
- Blanchette-Mackie E.J., Dwyer N.K., Barber T., Coxey R.A., Takeda T., Rondinone C.M., Theodorakis J.L., Greenberg A.S., Londos C. Perilipin is located on the surface layer of intracellular lipid droplets in adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 1995;36:1211–1226. - PubMed
-
- Brasaemle D.L., Barber T., Kimmel A.R., Londos C. Post-translational regulation of perilipin expressionstabilization by stored intracellular neutral lipids. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:9378–9387. - PubMed
-
- Das K., Lewis R.Y., Scherer P.E., Lisanti M.P. The membrane-spanning domains of caveolins-1 and -2 mediate the formation of caveolin hetero-oligomers. Implications for the assembly of caveolae membranes in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:18721–18728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

