Increased sensitivity to dextran sodium sulfate colitis in IRE1beta-deficient mice
- PMID: 11238559
- PMCID: PMC199427
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI11476
Increased sensitivity to dextran sodium sulfate colitis in IRE1beta-deficient mice
Abstract
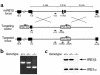
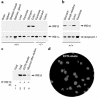
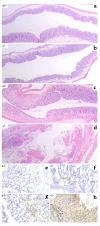
The epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract are exposed to toxins and infectious agents that can adversely affect protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and cause ER stress. The IRE1 genes are implicated in sensing and responding to ER stress signals. We found that epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract express IRE1beta, a specific isoform of IRE1. BiP protein, a marker of ER stress, was elevated in the colonic mucosa of IRE1beta(-/-) mice, and, when exposed to dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) to induce inflammatory bowel disease, mutant mice developed colitis 3-5 days earlier than did wild-type or IRE1beta(+/-) mice. The inflammation marker ICAM-1 was also expressed earlier in the colonic mucosa of DSS-treated IRE1beta(-/-) mice, indicating that the mutation had its impact early in the inflammatory process, before the onset of mucosal ulceration. These findings are consistent with a model whereby perturbations in ER function, which are normally mitigated by the activity of IRE1beta, participate in the development of colitis.
Figures
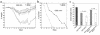
References
-
- Sartor RB. Cytokine regulation of experimental intestinal inflammation in genetically engineered and T-lymphocyte reconstituted rodents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1996;10(Suppl. 2):36–42. - PubMed
-
- Strober W, et al. Reciprocal IFN-gamma and TGF-beta responses regulate the occurrence of mucosal inflammation. Immunol Today. 1997;18:61–64. - PubMed
-
- Bhan AK, Mizoguchi E, Smith RN, Mizoguchi A. Colitis in transgenic and knockout animals as models of human inflammatory bowel disease. Immunol Rev. 1999;169:195–207. - PubMed
-
- Sadlack B, et al. Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell. 1993;75:253–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

