Overexpression of SH2-containing inositol phosphatase 2 results in negative regulation of insulin-induced metabolic actions in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via its 5'-phosphatase catalytic activity
- PMID: 11238900
- PMCID: PMC86709
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.5.1633-1646.2001
Overexpression of SH2-containing inositol phosphatase 2 results in negative regulation of insulin-induced metabolic actions in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via its 5'-phosphatase catalytic activity
Abstract
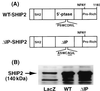
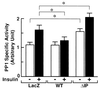
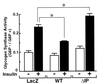
Phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase plays an important role in various metabolic actions of insulin including glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis. Although PI 3-kinase primarily functions as a lipid kinase which preferentially phosphorylates the D-3 position of phospholipids, the effect of hydrolysis of the key PI 3-kinase product PI 3,4,5-triphosphate [PI(3,4,5)P3] on these biological responses is unknown. We recently cloned rat SH2-containing inositol phosphatase 2 (SHIP2) cDNA which possesses the 5'-phosphatase activity to hydrolyze PI(3,4,5)P3 to PI 3,4-bisphosphate [PI(3,4)P2] and which is mainly expressed in the target tissues of insulin. To study the role of SHIP2 in insulin signaling, wild-type SHIP2 (WT-SHIP2) and 5'-phosphatase-defective SHIP2 (Delta IP-SHIP2) were overexpressed in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by means of adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. Early events of insulin signaling including insulin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor beta subunit and IRS-1, IRS-1 association with the p85 subunit, and PI 3-kinase activity were not affected by expression of either WT-SHIP2 or Delta IP-SHIP2. Because WT-SHIP2 possesses the 5'-phosphatase catalytic region, its overexpression marked by decreased insulin-induced PI(3,4,5)P3 production, as expected. In contrast, the amount of PI(3,4,5)P3 was increased by the expression of Delta IP-SHIP2, indicating that Delta IP-SHIP2 functions in a dominant-negative manner in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Both PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(3,4)P2 were known to possibly activate downstream targets Akt and protein kinase C lambda in vitro. Importantly, expression of WT-SHIP2 inhibited insulin-induced activation of Akt and protein kinase C lambda, whereas these activations were increased by expression of Delta IP-SHIP2 in vivo. Consistent with the regulation of downstream molecules of PI 3-kinase, insulin-induced 2-deoxyglucose uptake and Glut4 translocation were decreased by expression of WT-SHIP2 and increased by expression of Delta IP-SHIP2. In addition, insulin-induced phosphorylation of GSK-3beta and activation of PP1 followed by activation of glycogen synthase and glycogen synthesis were decreased by expression of WT-SHIP2 and increased by the expression of Delta IP-SHIP2. These results indicate that SHIP2 negatively regulates metabolic signaling of insulin via the 5'-phosphatase activity and that PI(3,4,5)P3 rather than PI(3,4)P2 is important for in vivo regulation of insulin-induced activation of downstream molecules of PI 3-kinase leading to glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis.
Figures

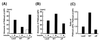
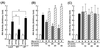
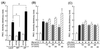
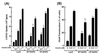
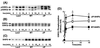
Similar articles
-
SH2-containing inositol phosphatase 2 negatively regulates insulin-induced glycogen synthesis in L6 myotubes.Diabetologia. 2001 Oct;44(10):1258-67. doi: 10.1007/s001250100645. Diabetologia. 2001. PMID: 11692174
-
Dual role of SRC homology domain 2-containing inositol phosphatase 2 in the regulation of platelet-derived growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I signaling in rat vascular smooth muscle cells.Endocrinology. 2003 Sep;144(9):4204-14. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0190. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12933696
-
Impact of Src homology 2-containing inositol 5'-phosphatase 2 on the regulation of insulin signaling leading to protein synthesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes cultured with excess amino acids.Endocrinology. 2004 Jul;145(7):3215-23. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1574. Epub 2004 Mar 24. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15044364
-
Lipid phosphatases as a possible therapeutic target in cases of type 2 diabetes and obesity.Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Dec;112(3):799-809. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.06.001. Epub 2006 Jul 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16842857 Review.
-
The SH2 domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase-2: SHIP2.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Nov;37(11):2260-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.05.003. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15964236 Review.
Cited by
-
SHIP2 (SH2 domain-containing inositol phosphatase 2) SH2 domain negatively controls SHIP2 monoubiquitination in response to epidermal growth factor.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 25;284(52):36062-36076. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.064923. Epub 2009 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19880507 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate regulates neurite initiation and dendrite morphogenesis via actin aggregation.Cell Res. 2017 Feb;27(2):253-273. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.13. Epub 2017 Jan 20. Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28106075 Free PMC article.
-
SKIP negatively regulates insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation and membrane ruffle formation.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Feb;23(4):1209-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1209-1220.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12556481 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol and PIP2/PIP3 Ratio: At the Crossroad of the Biodynamic Interface Between Cells and Their Microenvironment.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 20;15(3):451. doi: 10.3390/biom15030451. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PtdIns3P] is generated at the plasma membrane by an inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase: endogenous PtdIns3P can promote GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;26(16):6065-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00203-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16880518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi D R, Deak M, Casamayor A, Cawdwell F B, Morrice N, Norman D G, Gaffney P, Reese C B, MacDougall C N, Harbison D, Ashworth A, Bownes M. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1): structural and functional homology with Drosophila DSTPK61 kinase. Curr Biol. 1997;7:776–789. - PubMed
-
- Alessi D R, James S R, Downes C P, Holmes A B, Gaffney P R J, Reese C B, Cohen P. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Bα. Curr Biol. 1997;7:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Aman M J, Lamkin T D, Okada H, Kurosaki T, Ravichandran K S. The inositol phosphatase SHIP inhibits Akt/PKB activation in B cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:33922–33928. - PubMed
-
- Andjelkovic M, Alessi D R, Meier R, Fernandez A, Lamb N J C, Frech M, Cron P, Cohen P, Lucocq J M, Hemmings B A. Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31515–31524. - PubMed
-
- Brady M J, Bourbonais F J, Saltiel A R. The activation of glycogen synthase by insulin switches from kinase inhibition to phosphatase activation during adipogenesis in 3T3–L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14063–14066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
