Functional regions of human telomerase reverse transcriptase and human telomerase RNA required for telomerase activity and RNA-protein interactions
- PMID: 11238925
- PMCID: PMC86762
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.5.1888-1897.2001
Functional regions of human telomerase reverse transcriptase and human telomerase RNA required for telomerase activity and RNA-protein interactions
Abstract
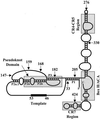
Telomerase is a specialized reverse transcriptase (RT) that is minimally composed of a protein catalytic subunit and an RNA component. The RNA subunit contains a short template sequence that directs the synthesis of DNA repeats at the ends of chromosomes. Human telomerase activity can be reconstituted in vitro by the expression of the human telomerase protein catalytic subunit (hTERT) in the presence of recombinant human telomerase RNA (hTR) in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) system. We analyzed telomerase activity and binding of hTR to hTERT in RRL by expressing different hTERT and hTR variants. hTRs containing nucleotide substitutions that are predicted to disrupt base pairing in the P3 helix of the pseudoknot weakly reconstituted human telomerase activity yet retained their ability to bind hTERT. Our results also identified two distinct regions of hTR that can independently bind hTERT in vitro. Furthermore, sequences or structures between nucleotides 208 and 330 of hTR (which include the conserved CR4-CR5 domain) were found to be important for hTERT-hTR interactions and for telomerase activity reconstitution. Human TERT carboxy-terminal amino acid deletions extending to motif E or the deletion of the first 280 amino acids abolished human telomerase activity without affecting the ability of hTERT to associate with hTR, suggesting that the RT and RNA binding functions of hTERT are separable. These results indicate that the reconstitution of human telomerase activity in vitro requires regions of hTERT that (i) are distinct from the conserved RT motifs and (ii) bind nucleotides distal to the hTR template sequence.
Figures

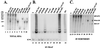


References
-
- Artandi S, DePinho R. A critical role for telomeres in suppressing and facilitating carcinogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2000;10:39–46. - PubMed
-
- Autexier C. Telomerase as a possible target for anticancer therapy. Chem Biol. 1999;6:R299–R303. - PubMed
-
- Autexier C, Greider C W. Boundary elements of the Tetrahymena telomerase RNA template and alignment domains. Genes Dev. 1995;15:2227–2239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
