P(II) signal transduction proteins, pivotal players in microbial nitrogen control
- PMID: 11238986
- PMCID: PMC99019
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.65.1.80-105.2001
P(II) signal transduction proteins, pivotal players in microbial nitrogen control
Abstract
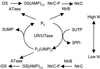
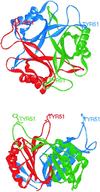
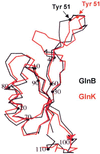
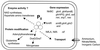
The P(II) family of signal transduction proteins are among the most widely distributed signal proteins in the bacterial world. First identified in 1969 as a component of the glutamine synthetase regulatory apparatus, P(II) proteins have since been recognized as playing a pivotal role in control of prokaryotic nitrogen metabolism. More recently, members of the family have been found in higher plants, where they also potentially play a role in nitrogen control. The P(II) proteins can function in the regulation of both gene transcription, by modulating the activity of regulatory proteins, and the catalytic activity of enzymes involved in nitrogen metabolism. There is also emerging evidence that they may regulate the activity of proteins required for transport of nitrogen compounds into the cell. In this review we discuss the history of the P(II) proteins, their structures and biochemistry, and their distribution and functions in prokaryotes. We survey data emerging from bacterial genome sequences and consider other likely or potential targets for control by P(II) proteins.
Figures
References
-
- Adler S P, Purich D, Stadtman E R. Cascade control of Escherichia coli glutamine synthetase: properties of the PIIregulatory protein and the uridylyltransferase-uridylylremoving enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1975;250:6264–6272. - PubMed
-
- Allikmets R, Gerrard B, Court D, Dean M. Cloning and organisation of the abc and mdl genes of Escherichia coli: relationship to eukaryotic multidrug resistance. Gene. 1993;136:231–236. - PubMed
-
- Amar M, Patriarca E J, Manco G, Bernard P, Riccio A, Lamberti A, Defez R, Iaccarino M. Regulation of nitrogen metabolism is altered in a glnB mutant strain of Rhizobium leguminosarum. Mol Microbiol. 1994;11:685–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

