Human papillomavirus DNA in plasma of patients with cervical cancer
- PMID: 11244579
- PMCID: PMC32170
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-1-2
Human papillomavirus DNA in plasma of patients with cervical cancer
Abstract
Background: Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a crucial etiological factor for cervical cancer (CC) development. From a diagnostic view-point, the consistent presence of HPV in CC allows the viral DNA to be used as a genetic marker. The aims of this study were to evaluate the presence, physical status and clinical significant of HPV DNA in circulation of CC patients.
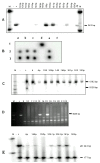
Results: Whereas 6 out of 50 (12%) HPV positive CC patients revealed plasma HPV DNA, it was detected in none of 20 normal controls or 13 HPV negative CC cases. The plasma DNA exhibited an HPV type identical to the HPV in the primary tumors and the DNA from both sources was integrated into host genome. Interestingly, several findings suggested an association between plasma HPV DNA and metastasis. First, three of the HPV DNA positive cases were CC patients with clinical stage IVB or recurrence with distance metastases (P = 0.001, RR = 15.67). Second, the amount of plasma HPV DNA from metastatic patients to be three times more than three other patients without metastases. Finally, the later cases had tendency to develop recurrence distant metastases within one year after complete treatment when compared with other HPV associated CC patients with the same stage but without the present of plasma HPV DNA.
Conclusions: The plasma HPV DNA originated from the CC, was associated with metastasis and could be used as a marker representing the circulating free CC DNA.
Figures
References
-
- Bosch FX, Manos MM, Munoz N, Sherman M, Jansen AM, Peto J, Schiffman MH, Moreno V, Kurman R, Shah KV. Prevalence of human papillomavirus in cervical cancer: a worldwide perspective International biological study on cervical cancer (IBSCC) Study Group. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995;87:796–802. doi: 10.1093/jnci/87.11.796. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schiffman MH, Bauer HM, Hoover RN, Glass AG, Cadell DM, Rush BB, Scott DR, Sherman ME, Kurman RJ, Wacholder S, Stanton CK, Manos MM. Epidemiologic evidence showing that human papillomavirus infection causes most cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85:958–964. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.12.958. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kubbutant MHG, Vousden KH. Role of E6 and E7 oncoproteins in HPV-induced anogenital malignancies. Semin Virol. 1996;7:295–304. doi: 10.1006/smvy.1996.0037. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

