Chronic exposure to nicotine upregulates the human (alpha)4((beta)2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function
- PMID: 11245666
- PMCID: PMC6762627
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-06-01819.2001
Chronic exposure to nicotine upregulates the human (alpha)4((beta)2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function
Abstract
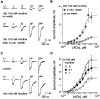
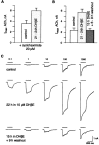
Widely expressed in the brain, the alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) is proposed to play a major role in the mechanisms that lead to and maintain nicotine addiction. Using the patch-clamp technique and pharmacological protocols, we examined the consequences of long-term exposure to 0.1-10 micrometer nicotine in K-177 cells expressing the major human brain alpha4beta2 receptor. The acetylcholine dose-response curves are biphasic and revealed both a high- and a low-affinity component with apparent EC(50) values of 1.6 and 62 micrometer. Ratios of receptors in the high- and low-affinity components are 25 and 75%, respectively. Chronic exposure to nicotine or nicotinic antagonists [dihydro-beta-erytroidine (DHbetaE) or methyllycaconitine (MLA)] increases the fraction of high-affinity receptors up to 70%. Upregulated acetylcholine-evoked currents increase by twofold or more and are less sensitive to desensitization. Functional upregulation is independent of protein synthesis as shown by the lack of effect of 20 micrometer cycloheximide. Single-channel currents recorded with 100 nm acetylcholine show predominantly high conductances (38.8 and 43.4 pS), whereas additional smaller conductances (16.7 and 23.5 pS) were observed with 30 micrometer acetylcholine. In addition, long-term exposure to dihydro-beta-erytroidine increases up to three times the frequency of channel openings. These data indicate, in contrast to previous studies, that human alpha4beta2 nAChRs are functionally upregulated by chronic nicotine exposure.
Figures





References
-
- Albuquerque EX, Pereira EF, Castro NG, Alkondon M, Reinhardt S, Schroder H, Maelicke A. Nicotinic receptor function in the mammalian central nervous system. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1995;757:48–72. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. I. Pharmacological and functional evidence for distinct structural subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:1455–1473. - PubMed
-
- Badio B, Daly JW. Epibatidine, a potent analgetic and nicotinic agonist. Mol Pharmacol. 1994;45:563–569. - PubMed
-
- Balfour DJ, Wright AE, Benwell ME, Birrell CE. The putative role of extra-synaptic mesolimbic dopamine in the neurobiology of nicotine dependence. Behav Brain Res. 2000;113:73–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
