From transforming growth factor-beta signaling to androgen action: identification of Smad3 as an androgen receptor coregulator in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 11248024
- PMCID: PMC30599
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.061305498
From transforming growth factor-beta signaling to androgen action: identification of Smad3 as an androgen receptor coregulator in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
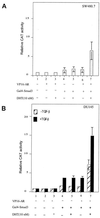
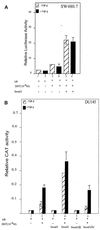
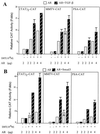
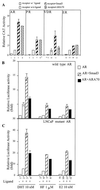
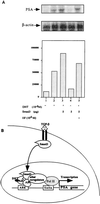
Although transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) has been identified to mainly inhibit cell growth, the correlation of elevated TGF-beta with increasing serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels in metastatic stages of prostate cancer has also been well documented. The molecular mechanism for these two contrasting effects of TGF-beta, however, remains unclear. Here we report that Smad3, a downstream mediator of the TGF-beta signaling pathway, functions as a coregulator to enhance androgen receptor (AR)-mediated transactivation. Compared with the wild-type AR, Smad3 acts as a strong coregulator in the presence of 1 nM 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone, 10 nM 17beta-estradiol, or 1 microM hydroxyflutamide for the LNCaP mutant AR (mtAR T877A), found in many prostate tumor patients. We further showed that endogenous PSA expression in LNCaP cells can be induced by 5alpha-dihydrotestosterone, and the addition of the Smad3 further induces PSA expression. Together, our findings establish Smad3 as an important coregulator for the androgen-signaling pathway and provide a possible explanation for the positive role of TGF-beta in androgen-promoted prostate cancer growth.
Figures
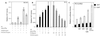

Similar articles
-
The androgen receptor represses transforming growth factor-beta signaling through interaction with Smad3.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jan 11;277(2):1240-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108855200. Epub 2001 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11707452
-
TGF-beta signaling and androgen receptor status determine apoptotic cross-talk in human prostate cancer cells.Prostate. 2008 Feb 15;68(3):287-95. doi: 10.1002/pros.20698. Prostate. 2008. PMID: 18163430
-
SMAD3 represses androgen receptor-mediated transcription.Cancer Res. 2001 Mar 1;61(5):2112-8. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11280774
-
Identification and characterization of androgen receptor associated coregulators in prostate cancer cells.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2001 Apr-Jun;15(2):123-9. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2001. PMID: 11501969 Review.
-
Functional analysis of androgen receptor N-terminal and ligand binding domain interacting coregulators in prostate cancer.J Formos Med Assoc. 2000 Dec;99(12):885-94. J Formos Med Assoc. 2000. PMID: 11155740 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Coding RNAs Set a New Phenotypic Frontier in Prostate Cancer Metastasis and Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 20;22(4):2100. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042100. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptors inhibit Smad3 transcriptional activity through Ap-1 transcription factors.Mol Cell Biochem. 2007 Dec;306(1-2):33-42. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9551-1. Epub 2007 Jul 28. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17660955
-
SMAD3 promotes expression and activity of the androgen receptor in prostate cancer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Apr 11;51(6):2655-2670. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad043. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36727462 Free PMC article.
-
H19 in Serum Extracellular Vesicles Reflects Resistance to AR Axis-targeted Therapy Among CRPC Patients.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2023 Sep-Oct;20(5):456-468. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20397. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37643783 Free PMC article.
-
Altered TNSALP expression and phosphate regulation contribute to reduced mineralization in mice lacking androgen receptor.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;28(24):7354-67. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00582-08. Epub 2008 Oct 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18838539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindzey J, Kumar M V, Grossman M, Young C, Tindall D J. Vitam Horm. 1994;49:383–432. - PubMed
-
- Chang C S, Kokontis J, Liao S T. Science. 1988;240:324–326. - PubMed
-
- Yeh S, Chang H C, Miyamoto H, Takatera H, Rahman M, Kang H Y, Thin T H, Lin H K, Chang C. Keio J Med. 1999;48:87–92. - PubMed
-
- Kang H Y, Yeh S, Fujimoto N, Chang C. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:8570–8576. - PubMed
-
- Fujimoto N, Yeh S, Kang H Y, Inui S, Chang H C, Mizokami A, Chang C. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:8316–8321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

