Indirect recognition of allopeptides promotes the development of cardiac allograft vasculopathy
- PMID: 11248069
- PMCID: PMC30644
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.051584498
Indirect recognition of allopeptides promotes the development of cardiac allograft vasculopathy
Abstract
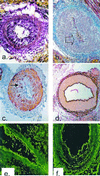
Graft loss from chronic rejection has become the major obstacle to the long-term success of whole organ transplantation. In cardiac allografts, chronic rejection is manifested as a diffuse and accelerated form of arteriosclerosis, termed cardiac allograft vasculopathy. It has been suggested that T-cell recognition of processed alloantigens (allopeptides) presented by recipient antigen-presenting cells through the indirect pathway of allorecognition plays a critical role in the development and progression of chronic rejection. However, definitive preclinical evidence to support this hypothesis is lacking. To examine the role of indirect allorecognition in a clinically relevant large animal model of cardiac allograft vasculopathy, we immunized MHC inbred miniature swine with synthetic polymorphic peptides spanning the alpha(1) domain of an allogeneic donor-derived swine leukocyte antigen class I gene. Pigs immunized with swine leukocyte antigen class I allopeptides showed in vitro proliferative responses and in vivo delayed-type hypersensitivity responses to the allogeneic peptides. Donor MHC class I disparate hearts transplanted into peptide-immunized cyclosporine-treated pigs not only rejected faster than unimmunized cyclosporine-treated controls (mean survival time = 5.5 +/-1.7 vs. 54.7 +/-3.8 days, P < 0.001), but they also developed obstructive fibroproliferative coronary artery lesions much earlier than unimmunized controls (<9 vs. >30 days). These results definitively link indirect allorecognition and cardiac allograft vasculopathy.
Figures


References
-
- Sayegh M H, Turka L A. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1813–1821. - PubMed
-
- Lechler R I, Lombardi G, Batchelor J R, Reinsmoen N L, Bach F H. Immunol Today. 1990;11:83–88. - PubMed
-
- Braun M Y, McCormack A, Webb G, Batchelor J R. Transplantation. 1993;55:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Ross R. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:115–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

