Intralymphatic immunization enhances DNA vaccination
- PMID: 11248073
- PMCID: PMC30648
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.051630798
Intralymphatic immunization enhances DNA vaccination
Abstract
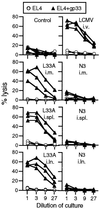
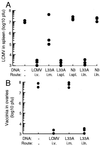
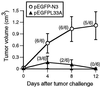
Although DNA vaccines have been shown to elicit potent immune responses in animal models, initial clinical trials in humans have been disappointing, highlighting a need to optimize their immunogenicity. Naked DNA vaccines are usually administered either i.m. or intradermally. The current study shows that immunization with naked DNA by direct injection into a peripheral lymph node enhances immunogenicity by 100- to 1,000-fold, inducing strong and biologically relevant CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. Because injection directly into a lymph node is a rapid and easy procedure in humans, these results have important clinical implications for DNA vaccination.
Figures


References
-
- Wolff J A, Malone R W, Williams P H, Chong W, Acsadi G, Jani A, Felgner P. Science. 1990;247:1465–1468. - PubMed
-
- Ulmer J B, Donnelly J J, Parker S E, Rhides G H, Felgner P L, Dwarki V J, Gromkoski S H, Deck R R, DeWitt C M, Friedman A. Science. 1993;259:1745–1749. - PubMed
-
- Ulmer J B, Deck R R, DeWitt C M, Fu T, Donnelly J J, Caulfield M J, Liu M A. Vaccine. 1997;8:839–845. - PubMed
-
- Xiang Z, Ertl H C. Immunity. 1995;2:129–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

