Peyer's patches are required for oral tolerance to proteins
- PMID: 11248075
- PMCID: PMC30650
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.061412598
Peyer's patches are required for oral tolerance to proteins
Abstract
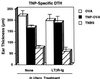
To clarify the role of Peyer's patches in oral tolerance induction, BALB/c mice were treated in utero with lymphotoxin beta-receptor Ig fusion protein to generate mice lacking Peyer's patches. When these Peyer's patch-null mice were fed 25 mg of ovalbumin (OVA) before systemic immunization, OVA-specific IgG Ab responses in serum and spleen were seen, in marked contrast to low responses in OVA-fed normal mice. Further, high T-cell-proliferative- and delayed-type hypersensitivity responses were seen in Peyer's patch-null mice given oral OVA before systemic challenge. Higher levels of CD4(+) T-cell-derived IFN-gamma, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10 syntheses were noted in Peyer's patch-null mice fed OVA, whereas OVA-fed normal mice had suppressed cytokine levels. In contrast, oral administration of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) to Peyer's patch-null mice resulted in reduced TNBS-specific serum Abs and splenic B cell antitrinitrophenyl Ab-forming cell responses after skin painting with picryl chloride. Further, when delayed-type hypersensitivity and splenic T cell proliferative responses were examined, Peyer's patch-null mice fed TNBS were unresponsive to hapten. Peyer's patch-null mice fed trinitrophenyl-OVA failed to induce systemic unresponsiveness to hapten or protein. These findings show that organized Peyer's patches are required for oral tolerance to proteins, whereas haptens elicit systemic unresponsiveness via the intestinal epithelial cell barrier.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Lack of oral tolerance in aging is due to sequential loss of Peyer's patch cell interactions.Int Immunol. 2003 Feb;15(2):145-58. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxg011. Int Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12578844
-
Alternate mucosal immune system: organized Peyer's patches are not required for IgA responses in the gastrointestinal tract.J Immunol. 2000 May 15;164(10):5184-91. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.10.5184. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10799877
-
Experimental granulomatous colitis in mice is abrogated by induction of TGF-beta-mediated oral tolerance.J Exp Med. 1996 Jun 1;183(6):2605-16. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2605. J Exp Med. 1996. PMID: 8676081 Free PMC article.
-
IL-12 and Th1 immune responses in human Peyer's patches.Trends Immunol. 2001 May;22(5):244-7. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4906(01)01892-0. Trends Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11323280 Review.
-
Peyer's patch organogenesis--cytokines rule, OK?Gut. 1997 Nov;41(5):707-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.41.5.707. Gut. 1997. PMID: 9414984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Active immunization using a single dose immunotherapeutic abates established EAE via IL-10 and regulatory T cells.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Feb;41(2):313-23. doi: 10.1002/eji.201041104. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21268002 Free PMC article.
-
Small bowel review: Normal physiology, part 2.Dig Dis Sci. 2003 Aug;48(8):1565-81. doi: 10.1023/a:1024724109128. Dig Dis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12924652 Review. No abstract available.
-
Oral probiotic promotes indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase- and TGF-β-Producing plasmacytoid dendritic cells to initiate protection against type 1 diabetes.Immunol Lett. 2021 Nov;239:12-19. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2021.07.009. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Immunol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34333043 Free PMC article.
-
Spi-B alleviates food allergy by securing mucosal barrier and immune tolerance in the intestine.Front Allergy. 2022 Oct 6;3:996657. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2022.996657. eCollection 2022. Front Allergy. 2022. PMID: 36277615 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal development and homeostasis require activation and apoptosis of diet-reactive T cells.J Clin Invest. 2019 Apr 2;129(5):1972-1983. doi: 10.1172/JCI98929. eCollection 2019 Apr 2. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30939122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGhee J R, Kiyono H. In: Fundamental Immunology. Paul W E, editor. San Diego: Academic; 1998. pp. 909–945.
-
- McGhee J R, Kiyono H. Infect Agents Dis. 1993;2:55–73. - PubMed
-
- Tomasi T B., Jr Transplantation. 1980;29:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Mayer L. Clin Immunol. 2000;94:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Wardrop R M, 3rd, Whitacre C C. Inflamm Res. 1999;48:106–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI 43197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK 44240/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE012242/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R29 DE012242/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- AI 35932/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 65299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK044240/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DE 09837/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI065299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI065298/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 65298/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI018958/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 18958/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DE 12242/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI043197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK 54781/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

