An essential role for nuclear receptors SXR/PXR in detoxification of cholestatic bile acids
- PMID: 11248086
- PMCID: PMC30661
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.051014398
An essential role for nuclear receptors SXR/PXR in detoxification of cholestatic bile acids
Abstract
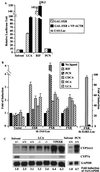
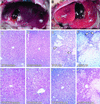
Hepatic hydroxylation is an essential step in the metabolism and excretion of bile acids and is necessary to avoid pathologic conditions such as cholestasis and liver damage. In this report, we demonstrate that the human xenobiotic receptor SXR (steroid and xenobiotic receptor) and its rodent homolog PXR (pregnane X receptor) serve as functional bile acid receptors in both cultured cells and animals. In particular, the secondary bile acid derivative lithocholic acid (LCA) is highly hepatotoxic and, as we show here, a metabolic substrate for CYP3A hydroxylation. By using combinations of knockout and transgenic animals, we show that activation of SXR/PXR is necessary and sufficient to both induce CYP3A enzymes and confer resistance to toxicity by LCA, as well as other xenotoxicants such as tribromoethanol and zoxazolamine. Therefore, we establish SXR and PXR as bile acid receptors and a role for the xenobiotic response in the detoxification of bile acids.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nuclear xeno-sensors as receptors for cholestatic bile acids: the second line of defense.Hepatology. 2002 Jan;35(1):232-4. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.0350232. Hepatology. 2002. PMID: 11786981 No abstract available.
-
The constitutive androstane receptor and pregnane X receptor function coordinately to prevent bile acid-induced hepatotoxicity.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 19;279(47):49517-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409041200. Epub 2004 Sep 8. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15358766
-
Intestinal detoxification limits the activation of hepatic pregnane X receptor by lithocholic acid.Drug Metab Dispos. 2010 Jan;38(1):143-9. doi: 10.1124/dmd.109.029306. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010. PMID: 19797606 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of xenobiotic and bile acid metabolism by the nuclear pregnane X receptor.J Lipid Res. 2002 Mar;43(3):359-64. J Lipid Res. 2002. PMID: 11893771 Review.
-
Regulation of cyp3a gene transcription by the pregnane x receptor.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002;42:1-23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.42.111901.111051. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 11807162 Review.
Cited by
-
Farnesoid X receptor alpha: a molecular link between bile acids and steroid signaling?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Dec;70(23):4511-26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1387-0. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23784309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does loss of bile acid homeostasis make mice melancholy?J Clin Invest. 2002 Oct;110(8):1067-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI16943. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12393840 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Protective effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on chenodeoxycholic acid-induced liver injury in hamsters.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Oct 7;13(37):5003-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i37.5003. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17854144 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Soft Spot and Pharmacokinetics: Functionalization of C-3 Position of an Eph-Ephrin Antagonist Featuring a Bile Acid Core as an Effective Strategy to Obtain Oral Bioavailability in Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Dec 28;15(1):41. doi: 10.3390/ph15010041. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35056098 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of PXR induces hypercholesterolemia in wild-type and accelerates atherosclerosis in apoE deficient mice.J Lipid Res. 2009 Oct;50(10):2004-13. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M800608-JLR200. Epub 2009 May 12. J Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 19436068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denison M S, Whitlock J P., Jr J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18175–18178. - PubMed
-
- Maurel P. In: Cytochrome P450: Metabolic and Toxicological Aspects. Ioannides C, editor. Boca Raton, FL: CRC; 1996. pp. 241–270.
-
- Selye H. J Pharm Sci. 1971;60:1–28. - PubMed
-
- Kliewer S A, Moore J T, Wade L, Staudinger J L, Jones M A, McKee D D, Oliver B M, Willson T M, Zetterstrom R H, Perlmann T, et al. Cell. 1998;92:73–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

