Signalling via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 is sufficient for lymphangiogenesis in transgenic mice
- PMID: 11250889
- PMCID: PMC145532
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.6.1223
Signalling via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 is sufficient for lymphangiogenesis in transgenic mice
Abstract
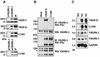
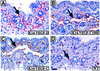
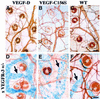
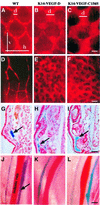
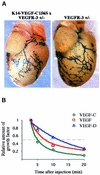
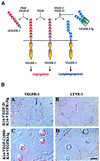
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3) has an essential role in the development of embryonic blood vessels; however, after midgestation its expression becomes restricted mainly to the developing lymphatic vessels. The VEGFR-3 ligand VEGF-C stimulates lymphangiogenesis in transgenic mice and in chick chorioallantoic membrane. As VEGF-C also binds VEGFR-2, which is expressed in lymphatic endothelia, it is not clear which receptors are responsible for the lymphangiogenic effects of VEGF-C. VEGF-D, which binds to the same receptors, has been reported to induce angiogenesis, but its lymphangiogenic potential is not known. In order to define the lymphangiogenic signalling pathway we have created transgenic mice overexpressing a VEGFR-3-specific mutant of VEGF-C (VEGF-C156S) or VEGF-D in epidermal keratinocytes under the keratin 14 promoter. Both transgenes induced the growth of lymphatic vessels in the skin, whereas the blood vessel architecture was not affected. Evidence was also obtained that these growth factors act in a paracrine manner in vivo. These results demonstrate that stimulation of the VEGFR-3 signal transduction pathway is sufficient to induce specifically lymphangiogenesis in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Achen M.G. et al. (2000) Monoclonal antibodies to vascular endothelial growth factor-D block its interactions with both VEGF receptor-2 and VEGF receptor-3. Eur. J. Biochem., 267, 2505–2515. - PubMed
-
- Aiello L.P., Pierce,E.A., Foley,E.D., Takagi,H., Chen,H., Riddle,L., Ferrara,N., King,G.L. and Smith,L.E. (1995) Suppression of retinal neovascularization in vivo by inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) using soluble VEGF-receptor chimeric proteins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 10457–10461. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Byrne C., Tainsky,M. and Fuchs,E. (1994) Programming gene expression in developing epidermis. Development, 120, 2369–2383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

