hRRN3 is essential in the SL1-mediated recruitment of RNA Polymerase I to rRNA gene promoters
- PMID: 11250903
- PMCID: PMC145519
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.6.1373
hRRN3 is essential in the SL1-mediated recruitment of RNA Polymerase I to rRNA gene promoters
Abstract
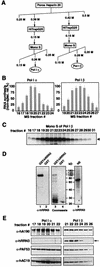
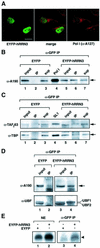
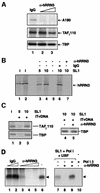
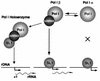
A crucial step in transcription is the recruitment of RNA polymerase to promoters. In the transcription of human rRNA genes by RNA Polymerase I (Pol I), transcription factor SL1 has a role as the essential core promoter binding factor. Little is known about the mechanism by which Pol I is recruited. We provide evidence for an essential role for hRRN3, the human homologue of a yeast Pol I transcription factor, in this process. We find that whereas the bulk of human Pol I complexes (I alpha) are transcriptionally inactive, hRRN3 defines a distinct subpopulation of Pol I complexes (I beta) that supports specific initiation of transcription. Human RRN3 interacts directly with TAF(I)110 and TAF(I)63 of promoter-selectivity factor SL1. Blocking this connection prevents recruitment of Pol I beta to the rDNA promoter. Furthermore, hRRN3 can be found in transcriptionally autonomous Pol I holoenzyme complexes. We conclude that hRRN3 functions to recruit initiation-competent Pol I to rRNA gene promoters. The essential role for hRRN3 in linking Pol I to SL1 suggests a mechanism for growth control of Pol I transcription.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A step subsequent to preinitiation complex assembly at the ribosomal RNA gene promoter is rate limiting for human RNA polymerase I-dependent transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Apr;21(8):2641-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.8.2641-2649.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11283244 Free PMC article.
-
SV40 large T antigen binds to the TBP-TAF(I) complex SL1 and coactivates ribosomal RNA transcription.Genes Dev. 1997 Jun 15;11(12):1605-17. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.12.1605. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9203586
-
The recruitment of RNA polymerase I on rDNA is mediated by the interaction of the A43 subunit with Rrn3.EMBO J. 2000 Oct 16;19(20):5473-82. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.20.5473. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 11032814 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA polymerase I transcription machinery.Biochem Soc Symp. 2006;(73):203-16. doi: 10.1042/bss0730203. Biochem Soc Symp. 2006. PMID: 16626300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA polymerase I termination: Where is the end?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar-Apr;1829(3-4):306-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.10.007. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23092677 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA binding by the ribosomal DNA transcription factor rrn3 is essential for ribosomal DNA transcription.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 29;288(13):9135-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.444265. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23393135 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptional activity of RNA polymerase I is a key determinant for the level of all ribosome components.Genes Dev. 2006 Aug 1;20(15):2030-40. doi: 10.1101/gad.386106. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16882981 Free PMC article.
-
Rrn3 gene knockout affects ethanol-induced locomotion in adult heterozygous zebrafish.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Feb;239(2):621-630. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-06056-7. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35006303
-
New roles for Dicer in the nucleolus and its relevance to cancer.Cell Cycle. 2017 Sep 17;16(18):1643-1653. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1361568. Epub 2017 Aug 28. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28846478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repression of class I transcription by cadmium is mediated by the protein phosphatase 2A.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jul;41(12):6087-97. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt335. Epub 2013 May 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23640330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bateman E. and Paule,M.R. (1986) Regulation of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA transcription by RNA polymerase modification. Cell, 47, 445–450. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann H., Chen,J.L., O’Brien,T. and Tjian,R. (1995) Coactivator and promoter-selective properties of RNA polymerase I TAFs. Science, 270, 1506–1509. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.D. and Jackson,S.P. (1998) Transcription in Archaea. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol., 63, 41–51. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.P., Learned,R.M., Jantzen,H.M. and Tjian,R. (1988) Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science, 241, 1192–1197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

