hRRN3 is essential in the SL1-mediated recruitment of RNA Polymerase I to rRNA gene promoters
- PMID: 11250903
- PMCID: PMC145519
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.6.1373
hRRN3 is essential in the SL1-mediated recruitment of RNA Polymerase I to rRNA gene promoters
Abstract
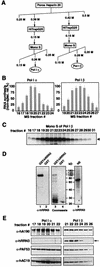
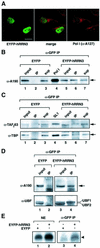
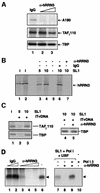
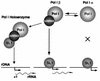
A crucial step in transcription is the recruitment of RNA polymerase to promoters. In the transcription of human rRNA genes by RNA Polymerase I (Pol I), transcription factor SL1 has a role as the essential core promoter binding factor. Little is known about the mechanism by which Pol I is recruited. We provide evidence for an essential role for hRRN3, the human homologue of a yeast Pol I transcription factor, in this process. We find that whereas the bulk of human Pol I complexes (I alpha) are transcriptionally inactive, hRRN3 defines a distinct subpopulation of Pol I complexes (I beta) that supports specific initiation of transcription. Human RRN3 interacts directly with TAF(I)110 and TAF(I)63 of promoter-selectivity factor SL1. Blocking this connection prevents recruitment of Pol I beta to the rDNA promoter. Furthermore, hRRN3 can be found in transcriptionally autonomous Pol I holoenzyme complexes. We conclude that hRRN3 functions to recruit initiation-competent Pol I to rRNA gene promoters. The essential role for hRRN3 in linking Pol I to SL1 suggests a mechanism for growth control of Pol I transcription.
Figures


References
-
- Bateman E. and Paule,M.R. (1986) Regulation of eukaryotic ribosomal RNA transcription by RNA polymerase modification. Cell, 47, 445–450. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann H., Chen,J.L., O’Brien,T. and Tjian,R. (1995) Coactivator and promoter-selective properties of RNA polymerase I TAFs. Science, 270, 1506–1509. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.D. and Jackson,S.P. (1998) Transcription in Archaea. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol., 63, 41–51. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.P., Learned,R.M., Jantzen,H.M. and Tjian,R. (1988) Functional cooperativity between transcription factors UBF1 and SL1 mediates human ribosomal RNA synthesis. Science, 241, 1192–1197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

