The DnaB.DnaC complex: a structure based on dimers assembled around an occluded channel
- PMID: 11250911
- PMCID: PMC145514
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.6.1462
The DnaB.DnaC complex: a structure based on dimers assembled around an occluded channel
Abstract
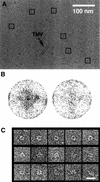
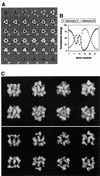
Replicative helicases are motor proteins that unwind DNA at replication forks. Escherichia coli DnaB is the best characterized member of this family of enzymes. We present the 26 A resolution three-dimensional structure of the DnaB hexamer in complex with its loading partner, DnaC, obtained from cryo-electron microscopy. Analysis of the volume brings insight into the elaborate way the two proteins interact, and provides a structural basis for control of the symmetry state and inactivation of the helicase by DnaC. The complex is arranged on the basis of interactions among DnaC and DnaB dimers. DnaC monomers are observed for the first time to arrange as three dumb-bell-shaped dimers that interlock into one of the faces of the helicase. This could be responsible for the freezing of DnaB in a C(3) architecture by its loading partner. The central channel of the helicase is almost occluded near the end opposite to DnaC, such that even single-stranded DNA could not pass through. We propose that the DnaB N-terminal domain is located at this face.
Figures


References
-
- Baker T.A. and Bell,S.P. (1998) Polymerases and the replisome: machines within machines. Cell, 92, 295–305. - PubMed
-
- Baker T.A., Sekimizu,K., Funnell,B.E. and Kornberg,A. (1986) Extensive unwinding of the plasmid template during staged enzymatic initiation of DNA replication from the origin of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Cell, 45, 53–64. - PubMed
-
- Bárcena M. (2000) Análisis estructural del polimorfismo cuaternario en las helicasas replicativas y del complejo DnaB⋅DnaC de Escherichia coli. PhD thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain.
-
- Biswas S.B., Chen,P.-H. and Biswas,E.E. (1994) Structure and function of Escherichia coli DnaB protein: role of the N-terminal domain in helicase activity. Biochemistry, 33, 11307–11314. - PubMed
-
- Chang P. and Marians,K.J. (2000) Identification of a region of Escherichia coli DnaB required for functional interaction with DnaG at the replication fork. J. Biol. Chem., 275, 26187–26195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

