Polycystin-2, the protein mutated in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), is a Ca2+-permeable nonselective cation channel
- PMID: 11252306
- PMCID: PMC14729
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.98.3.1182
Polycystin-2, the protein mutated in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), is a Ca2+-permeable nonselective cation channel
Abstract
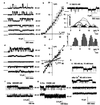
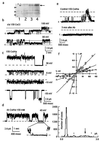
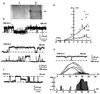
Defects in polycystin-2, a ubiquitous transmembrane glycoprotein of unknown function, is a major cause of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), whose manifestation entails the development of fluid-filled cysts in target organs. Here, we demonstrate that polycystin-2 is present in term human syncytiotrophoblast, where it behaves as a nonselective cation channel. Lipid bilayer reconstitution of polycystin-2-positive human syncytiotrophoblast apical membranes displayed a nonselective cation channel with multiple subconductance states, and a high perm-selectivity to Ca2+. This channel was inhibited by anti-polycystin-2 antibody, Ca2+, La3+, Gd3+, and the diuretic amiloride. Channel function by polycystin-2 was confirmed by patch-clamping experiments of polycystin-2 heterologously infected Sf9 insect cells. Further, purified insect cell-derived recombinant polycystin-2 and in vitro translated human polycystin-2 had similar ion channel activity. The polycystin-2 channel may be associated with fluid accumulation and/or ion transport regulation in target epithelia, including placenta. Dysregulation of this channel provides a mechanism for the onset and progression of ADPKD.
Figures


Comment in
-
Polycystic kidney disease: In danger of being X-rated?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jan 30;98(3):790-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.98.3.790. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11158545 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dalgaard O Z. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1957;328:1–255. - PubMed
-
- Arnaout M A. Annu Rev Med. 2001;52:93–123. - PubMed
-
- Grantham J J. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993;3:1843–1857. - PubMed
-
- The European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium. Cell. 1994;77:881–894. - PubMed
-
- The International Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium. Cell. 1995;81:289–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

