A genomewide screen in multiplex rheumatoid arthritis families suggests genetic overlap with other autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 11254450
- PMCID: PMC1275647
- DOI: 10.1086/319518
A genomewide screen in multiplex rheumatoid arthritis families suggests genetic overlap with other autoimmune diseases
Abstract
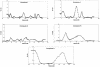
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune/inflammatory disorder with a complex genetic component. We report the first major genomewide screen of multiplex families with RA gathered in the United States. The North American Rheumatoid Arthritis Consortium, using well-defined clinical criteria, has collected 257 families containing 301 affected sibling pairs with RA. A genome screen for allele sharing was performed, using 379 microsatellite markers. A nonparametric analysis using SIBPAL confirmed linkage of the HLA locus to RA (P < .00005), with lambdaHLA = 1.79. However, the analysis also revealed a number of non-HLA loci on chromosomes 1 (D1S235), 4 (D4S1647), 12 (D12S373), 16 (D16S403), and 17 (D17S1301), with evidence for linkage at a significance level of P<.005. Analysis of X-linked markers using the MLOD method from ASPEX also suggests linkage to the telomeric marker DXS6807. Stratifying the families into white or seropositive subgroups revealed some additional markers that showed improvement in significance over the full data set. Several of the regions that showed evidence for nominal significance (P < .05) in our data set had previously been implicated in RA (D16S516 and D17S1301) or in other diseases of an autoimmune nature, including systemic lupus erythematosus (D1S235), inflammatory bowel disease (D4S1647, D5S1462, and D16S516), multiple sclerosis (D12S1052), and ankylosing spondylitis (D16S516). Therefore, genes in the HLA complex play a major role in RA susceptibility, but several other regions also contribute significantly to overall genetic risk.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- ASPEX, ftp://lahmed.stanford.edu/pub/aspex/index.html (for ASPEX software package)
-
- Marshfield, http://www.marshmed.org/genetics/ (for markers and PCR protocol)
-
- NARAC, http://www.naracdata.org/ (for summary marker data, information about obtaining DNA samples, and further results of genomewide screen)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for RA [180300], SLE [152700], IBD [266600]), MS [126200], and AS [106300])
-
- Statlib, http://www.statlab.uni-heidelberg.de/mirrors/statlib/apstat/.index.html (for software by Dunnet [reference 251])
References
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS, Medsger TA Jr, Mitchell DM, Neustadt DH, Pinals RS, Schaller JG, Sharp JT, Wilder RL, Hunder GG (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324 - PubMed
-
- Barton A, Eyre S, Myerscough A, Silman A, Ollier W, Worthington J (2000) A novel RA susceptibility locus on chromosome 17 identified using syntenic mapping approaches. Arthritis Rheum Suppl 43:1225
-
- Brown BW, Russell K (1997) Methods correcting for multiple testing: operating characteristics. Stat Med 16:2511–2558 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

