Micrococcus luteus teichuronic acids activate human and murine monocytic cells in a CD14- and toll-like receptor 4-dependent manner
- PMID: 11254554
- PMCID: PMC98126
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2025-2030.2001
Micrococcus luteus teichuronic acids activate human and murine monocytic cells in a CD14- and toll-like receptor 4-dependent manner
Abstract
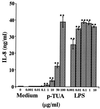
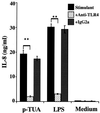
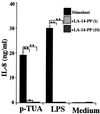
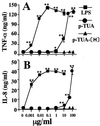
Teichuronic acid (TUA), a component of the cell walls of the gram-positive organism Micrococcus luteus (formerly Micrococcus lysodeikticus), induced inflammatory cytokines in C3H/HeN mice but not in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-resistant C3H/HeJ mice that have a defect in the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) gene, both in vivo and in vitro, similarly to LPS (T. Monodane, Y. Kawabata, S. Yang, S. Hase, and H. Takada, J. Med. Microbiol. 50:4-12, 2001). In this study, we found that purified TUA (p-TUA) induced tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) in murine monocytic J774.1 cells but not in mutant LR-9 cells expressing membrane CD14 at a lower level than the parent J774.1 cells. The TNF-alpha-inducing activity of p-TUA in J774.1 cells was completely inhibited by anti-mouse CD14 monoclonal antibody (MAb). p-TUA also induced interleukin-8 (IL-8) in human monocytic THP-1 cells differentiated to macrophage-like cells expressing CD14. Anti-human CD14 MAb, anti-human TLR4 MAb, and synthetic lipid A precursor IV(A), an LPS antagonist, almost completely inhibited the IL-8-inducing ability of p-TUA, as well as LPS, in the differentiated THP-1 cells. Reduced p-TUA did not exhibit any activities in J774.1 or THP-1 cells. These findings strongly suggested that M. luteus TUA activates murine and human monocytic cells in a CD14- and TLR4-dependent manner, similar to LPS.
Figures
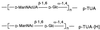

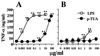
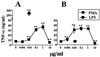
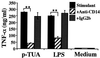

Similar articles
-
Synergistic effect of muramyldipeptide with lipopolysaccharide or lipoteichoic acid to induce inflammatory cytokines in human monocytic cells in culture.Infect Immun. 2001 Apr;69(4):2045-53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2045-2053.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11254557 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of CD14 and toll-like receptors in activation of human monocytes by Aspergillus fumigatus hyphae.Infect Immun. 2001 Apr;69(4):2402-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.4.2402-2406.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11254600 Free PMC article.
-
Monocytic cell activation by Nonendotoxic glycoprotein from Prevotella intermedia ATCC 25611 is mediated by toll-like receptor 2.Infect Immun. 2001 Aug;69(8):4951-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.4951-4957.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11447173 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of endotoxin activity by muramyldipeptide.J Endotoxin Res. 2002;8(5):337-42. doi: 10.1179/096805102125000669. J Endotoxin Res. 2002. PMID: 12537692 Review.
-
Expression and involvement of Toll-like receptors (TLR)2, TLR4, and CD14 in monocyte TNF-alpha production induced by lipopolysaccharides from Neisseria meningitidis.Med Sci Monit. 2003 Aug;9(8):BR316-24. Med Sci Monit. 2003. PMID: 12942028
Cited by
-
From Classical to Unconventional: The Immune Receptors Facilitating Platelet Responses to Infection and Inflammation.Biology (Basel). 2020 Oct 20;9(10):343. doi: 10.3390/biology9100343. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33092021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial endosymbionts of Pyrodinium bahamense var. compressum.Microb Ecol. 2006 Nov;52(4):756-64. doi: 10.1007/s00248-006-9128-7. Epub 2006 Aug 31. Microb Ecol. 2006. PMID: 16944340
-
The RHIM of the Immune Adaptor Protein TRIF Forms Hybrid Amyloids with Other Necroptosis-Associated Proteins.Molecules. 2022 May 24;27(11):3382. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113382. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684320 Free PMC article.
-
N-O chemistry for antibiotics: discovery of N-alkyl-N-(pyridin-2-yl)hydroxylamine scaffolds as selective antibacterial agents using nitroso Diels-Alder and ene chemistry.J Med Chem. 2011 Oct 13;54(19):6843-58. doi: 10.1021/jm200794r. Epub 2011 Sep 15. J Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21859126 Free PMC article.
-
Potential effects of microbial air quality on the number of new cases of diabetes type 1 in children in two regions of Poland: a pilot study.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Jul 29;12:2323-2334. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S207138. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31534351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi Y, Satokawa C, Saeki M, Ohno N, Tamura H, Tanaka S, Yadomae T. Inhibition by a CD14 monoclonal antibody of lipopolysaccharide binding to murine macrophages. J Endotoxin Res. 1999;5:139–146.
-
- Aderem A, Ulevitch R J. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000;406:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Albertson D, Natsios G A, Gleckman R. Septic shock with Micrococcus luteus. Arch Intern Med. 1978;138:487–488. - PubMed
-
- Arbour N C, Lorenz E, Schutte B C, Zabner J, Kline J N, Jones M, Frees K, Watt J L, Schwartz D A. TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat Genet. 2000;25:187–191. - PubMed
-
- Dürst U N, Bruder E, Egloff L, Wust J, Schneider J, Hirzel H O. Micrococcus luteus: Ein seltener Erreger einer Klappenprothesenendokarditis. Z Kardiol. 1991;80:294–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

