Composing life
- PMID: 11256602
- PMCID: PMC1083737
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvd063
Composing life
Abstract
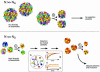
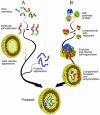
Textbooks often assert that life began with specialized complex molecules, such as RNA, that are capable of making their own copies. This scenario has serious difficulties, but an alternative has remained elusive. Recent research and computer simulations have suggested that the first steps toward life may not have involved biopolymers. Rather, non-covalent protocellular assemblies, generated by catalyzed recruitment of diverse amphiphilic and hydrophobic compounds, could have constituted the first systems capable of information storage, inheritance and selection. A complex chain of evolutionary events, yet to be deciphered, could then have led to the common ancestors of today's free-living cells, and to the appearance of DNA, RNA and protein enzymes.
Figures

References
-
- Allamandola L.J., Hudgins, D.M., Bauschlicher, C.W.,Jr and Langhoff, S.R. (1999) Carbon chain abundance in the diffuse interstellar medium. Astron. Astrophys., 352, 659–664. - PubMed
-
- Altreuter D.H. and Clark, D.S. (1999) Combinatorial biocatalysis: taking the lead from nature. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 10, 130–136. - PubMed
-
- Amend J.P. and Shock, E.L. (1998) Energetics of amino acid synthesis in hydrothermal ecosystems. Science, 281, 1659–1662. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann P., Luisi, P. and Lang, J. (1992) Autocatalytic self-replicating micelles as models for prebiotic structures. Nature, 357, 57–59.
-
- Blocher M., Liu, D., Walde, P. and Luisi, P.L. (1999) Liposome-assisted selective polycondensation of α-amino acids and peptides. Macromolecules, 32, 7332–7334.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

