The G x U wobble base pair. A fundamental building block of RNA structure crucial to RNA function in diverse biological systems
- PMID: 11256617
- PMCID: PMC1083677
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvd001
The G x U wobble base pair. A fundamental building block of RNA structure crucial to RNA function in diverse biological systems
Abstract
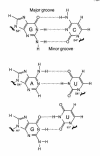
The G x U wobble base pair is a fundamental unit of RNA secondary structure that is present in nearly every class of RNA from organisms of all three phylogenetic domains. It has comparable thermodynamic stability to Watson-Crick base pairs and is nearly isomorphic to them. Therefore, it often substitutes for G x C or A x U base pairs. The G x U wobble base pair also has unique chemical, structural, dynamic and ligand-binding properties, which can only be partially mimicked by Watson-Crick base pairs or other mispairs. These features mark sites containing G x U pairs for recognition by proteins and other RNAs and allow the wobble pair to play essential functional roles in a remarkably wide range of biological processes.
Figures


References
-
- Abramovitz D.L., Friedman, R.A. and Pyle, A.M. (1996) Catalytic role of 2′-hydroxyl groups within a group II intron active site. Science, 271, 1410–1413. - PubMed
-
- Allain F.H.-T. and Varani, G. (1995b) Structure of the P1 helix from group I self splicing introns. J. Mol. Biol., 250, 333–353. - PubMed
-
- Cate J.H. and Doudna, J.A. (1996) Metal-binding sites in the major groove of a large ribozyme domain. Structure, 4, 1221–1229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

