Quinolone resistance in Staphylococci: activities of new nonfluorinated quinolones against molecular targets in whole cells and clinical isolates
- PMID: 11257024
- PMCID: PMC90433
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.4.1115-1120.2001
Quinolone resistance in Staphylococci: activities of new nonfluorinated quinolones against molecular targets in whole cells and clinical isolates
Abstract
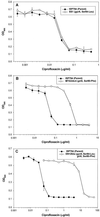
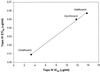
The activity of three new, 8-methoxy-nonfluorinated quinolones (NFQs) against multiple-drug-resistant staphylococci was investigated. First, using Staphylococcus aureus strains containing point mutations in the serine 84-80 hot spots of the target genes (gyrA and grlA), cell growth inhibition potencies of the NFQs as a result of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV inhibition were estimated and compared with those of known fluoroquinolones. The NFQs and clinafloxacin showed higher affinities toward both the targets than ciprofloxacin, trovafloxacin and gatifloxacin. Furthermore, the ratio of the calculated affinity parameter for DNA gyrase to that for topoisomerase IV was lower in the case of the NFQs, clinafloxacin, and gatifloxacin than in the case of ciprofloxacin and trovafloxacin. These results suggest that the former group of quinolones is better able to exploit both the targets. Next, using clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA; n = 34) and coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS; n = 24), the NFQs and clinafloxacin were shown to be more potent (MIC at which 90% of the isolates are inhibited [MIC90] = 2 microg/ml for MRSA and 0.5 microg/ml for CoNS) than ciprofloxacin, trovafloxacin, and gatifloxacin (MIC90 = 16 to >64 microg/ml for MRSA and 4 to >32 microg/ml for CoNS). Bactericidal kinetics experiments, using two MRSA isolates, showed that exposure to the NFQs at four times the MIC reduced the bacterial counts (measured in CFU per milliliter) by > or =3 log units in 2 to 4 h. Overall, the NFQs and clinafloxacin were less susceptible than the other quinolones to existing mechanisms of quinolone resistance in staphylococci.
Figures
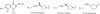
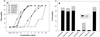


References
-
- Anderson V E, Zaniewski R P, Kaczmarek F S, Gootz T D, Osheroff N. Quinolones inhibit DNA religation mediated by Staphylococcus aureus topoisomerase IV. Changes in drug mechanism across evolutionary boundaries. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:35927–35932. - PubMed
-
- Canton E, Ramon M S, Jimenez M T, Martinez J P. Killing kinetics of four quinolones against gram-positive cocci. Chemotherapy. 1993;39:394–399. - PubMed
-
- Chen A Y, Lie L F. DNA topoisomerase: essential enzymes and lethal targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1994;34:191–218. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

