Protein unfolding by mitochondria. The Hsp70 import motor
- PMID: 11258479
- PMCID: PMC1083766
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvd093
Protein unfolding by mitochondria. The Hsp70 import motor
Abstract
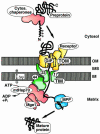
Protein unfolding is a key step in the import of some proteins into mitochondria and chloroplasts and in the degradation of regulatory proteins by ATP-dependent proteases. In contrast to protein folding, the reverse process has remained largely uninvestigated until now. This review discusses recent discoveries on the mechanism of protein unfolding during translocation into mitochondria. The mitochondria can actively unfold preproteins by unraveling them from the N-terminus. The central component of the mitochondrial import motor, the matrix heat shock protein 70, functions by both pulling and holding the preproteins.
Figures
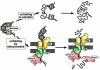
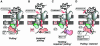



References
-
- Astumian R.D. (1997) Thermodynamics and kinetics of a Brownian motor. Science, 276, 917–922. - PubMed
-
- Bauer M.F., Hofmann, S., Neupert, W. and Brunner, M. (2000) Protein translocation into mitochondria: the role of TIM complexes. Trends Cell Biol., 10, 25–31. - PubMed
-
- Bömer U., Meijer, M., Guiard, B., Dietmeier, K., Pfanner, N. and Rassow, J. (1997) The sorting route of cytochrome b2 branches from the general mitochondrial import pathway at the preprotein translocase of the inner membrane. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 30439–30446. - PubMed
-
- Bömer U., Maarse, A.C., Martin, F., Geissler, A., Merlin, A., Schönfisch, B., Meijer, M., Pfanner, N. and Rassow, J. (1998) Separation of structural and dynamic functions of the mitochondrial translocase: Tim44 is crucial for the inner membrane import sites in translocation of tightly folded domains, but not of loosely folded preproteins. EMBO J., 17, 4226–4237. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Branden C. and Tooze, J. (1998) Introduction to Protein Structure. Garland, New York.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

