The archaeal TFIIEalpha homologue facilitates transcription initiation by enhancing TATA-box recognition
- PMID: 11258705
- PMCID: PMC1083817
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kve021
The archaeal TFIIEalpha homologue facilitates transcription initiation by enhancing TATA-box recognition
Abstract
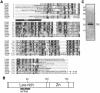
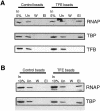
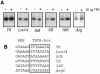
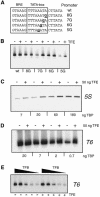
Transcription from many archaeal promoters can be reconstituted in vitro using recombinant TATA-box binding protein (TBP) and transcription factor B (TFB)--homologues of eukaryal TBP and TFIIB--together with purified RNA polymerase (RNAP). However, all archaeal genomes sequenced to date reveal the presence of TFE, a homologue of the alpha-subunit of the eukaryal general transcription factor, TFIIE. We show that, while TFE is not absolutely required for transcription in the reconstituted in vitro system, it nonetheless plays a stimulatory role on some promoters and under certain conditions. Mutagenesis of the TATA box or reduction of TBP concentration in transcription reactions sensitizes a promoter to TFE addition. Conversely, saturating reactions with TBP de-sensitizes promoters to TFE. These results suggest that TFE facilitates or stabilizes interactions between TBP and the TATA box.
Figures
References
-
- Bell S.D. and Jackson, S.P. (1998a) Transcription and translation in Archaea: a mosaic of eukaryal and bacterial features. Trends. Microbiol., 6, 222–228. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.D. and Jackson, S.P. (1998b) Transcription in Archaea. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol., 63, 41–51. - PubMed
-
- Bell S.D. and Jackson, S.P. (2000) The role of transcription factor B in transcription initiation and promoter clearance in the archaeon Sulfolobus acidocaldarius.J. Biol. Chem., 275, 12934–12940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

