The human brm protein is cleaved during apoptosis: the role of cathepsin G
- PMID: 11259672
- PMCID: PMC31135
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.071057398
The human brm protein is cleaved during apoptosis: the role of cathepsin G
Abstract
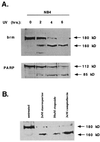
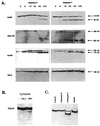
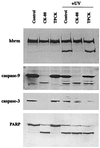
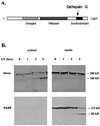
The human brm (hbrm) protein (homologue of the Drosophila melanogaster brahma and Saccharomyces cervisiae SNF-2 proteins) is part of a polypeptide complex believed to regulate chromatin conformation. We have shown that the hbrm protein is cleaved in NB4 leukemic cells after induction of apoptosis by UV-irradiation, DNA damaging agents, or staurosporine. Because hbrm is found only in the nucleus, we have investigated the nature of the proteases that may regulate the degradation of this protein during apoptosis. In an in vitro assay, the hbrm protein could not be cleaved by caspase-3, -7, or -6, the "effector" caspases generally believed to carry out the cleavage of nuclear protein substrates. In contrast, we find that cathepsin G, a granule enzyme found in NB4 cells, cleaves hbrm in a pattern similar to that observed in vivo during apoptosis. In addition, a peptide inhibitor of cathepsin G blocks hbrm cleavage during apoptosis but does not block activation of caspases or cleavage of the nuclear protein polyADP ribose polymerase (PARP). Although localized in granules and in the Golgi complex in untreated cells, cathepsin G becomes diffusely distributed during apoptosis. Cleavage by cathepsin G removes a 20-kDa fragment containing a bromodomain from the carboxyl terminus of hbrm. This cleavage disrupts the association between hbrm and the nuclear matrix; the 160-kDa hbrm cleavage fragment is less tightly associated with the nuclear matrix than full-length hbrm.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of the necrotic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP-1): implication of lysosomal proteases.Cell Death Differ. 2001 Jun;8(6):588-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400851. Cell Death Differ. 2001. PMID: 11536009
-
Inflammation-related neutrophil proteases, cathepsin G and elastase, function as insulin-like growth factor binding protein proteases.Growth Horm IGF Res. 1999 Aug;9(4):241-53. doi: 10.1054/ghir.1999.0115. Growth Horm IGF Res. 1999. PMID: 10512690
-
A human homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae SNF2/SWI2 and Drosophila brm genes potentiates transcriptional activation by the glucocorticoid receptor.EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4279-90. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06112.x. EMBO J. 1993. PMID: 8223438 Free PMC article.
-
The hbrm and BRG-1 proteins, components of the human SNF/SWI complex, are phosphorylated and excluded from the condensed chromosomes during mitosis.EMBO J. 1996 Jul 1;15(13):3394-402. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8670841 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolysis of factor V by cathepsin G and elastase indicates that cleavage at Arg1545 optimizes cofactor function by facilitating factor Xa binding.Biochemistry. 1998 Aug 25;37(34):11896-906. doi: 10.1021/bi980520v. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9718313
Cited by
-
Cathepsin G induces cell aggregation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via a 2-step mechanism: catalytic site-independent binding to the cell surface and enzymatic activity-dependent induction of the cell aggregation.Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:456462. doi: 10.1155/2012/456462. Epub 2012 Jul 8. Mediators Inflamm. 2012. PMID: 22919124 Free PMC article.
-
Brahma is essential for Drosophila intestinal stem cell proliferation and regulated by Hippo signaling.Elife. 2013 Oct 15;2:e00999. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00999. Elife. 2013. PMID: 24137538 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear degradation dynamics in a nonapoptotic programmed cell death.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Feb;27(2):711-724. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0382-x. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 31285547 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation patterns of Brahma during spermatogenesis and oogenesis: potential implications.Fertil Steril. 2011 Jan;95(1):382-4. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.05.064. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Fertil Steril. 2011. PMID: 20719309 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of cathepsin G expression in severe atopic dermatitis following medium-dose UVA1 phototherapy.BMC Dermatol. 2002 Aug 30;2:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-5945-2-12. BMC Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 12204095 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Khavare P A, Peterson C L, Tamkun J W, Mendel D B, Crabtree G R. Nature (London) 1993;366:170–174. - PubMed
-
- Peterson C L, Herskowitz I. Cell. 1992;68:573–583. - PubMed
-
- Hirschhorn J N, Brown S A, Clark C D, Winston F. Genes Dev. 1992;6:2288–2298. - PubMed
-
- Peterson C L, Tamkun J W. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995;20:143–147. - PubMed
-
- Laurent B C, Carlson M. Genes Dev. 1992;6:1707–1715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

