Changes of cone electroretinograms to colour flash stimuli after successful retinal detachment surgery
- PMID: 11264128
- PMCID: PMC1723907
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.85.4.410
Changes of cone electroretinograms to colour flash stimuli after successful retinal detachment surgery
Abstract
Aim: To examine the changes in the short wavelength (S) and mixed long (L) and middle (M) wavelength sensitive cone (L,M-cone) electroretinograms (ERGs) after successful retinal detachment surgery.
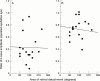
Methods: Cone ERGs elicited by different colour flashes were recorded from 19 eyes with unilateral rhegmatogenous retinal detachment treated successfully by conventional buckling surgery. Ganzfeld colour flashes on a bright white background were used to elicit S-cone and L,M-cone ERGs. The ratio (operated eye/fellow eye) of the S-cone b-wave elicited by a 450 nm stimulus and the ratio (operated eye/fellow eye) of the L,M-cone b-wave elicited by a 633 nm stimulus were evaluated preoperatively and 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery.
Results: Preoperatively, no significant difference was observed between the ratio of the S-cone ERG amplitudes and the ratio of the L,M-cone ERG amplitudes. Postoperatively, the ratio of the L,M-cone ERGs increased significantly over the preoperative value (p=0.001) but the ratio of the S-cone ERG did not improve. There were significant differences between the ratios of the S-cone and the L,M-cone ERGs at 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery. The postoperative recovery of the S-cone ERG was significantly greater in eyes treated within 4 weeks after the onset of the detachment than in eyes treated later than 4 weeks.
Conclusions: These results indicate that the impairment of the L,M-cone system caused by retinal detachment may be reversible. However, the S-cone system may have more profound permanent damage.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
