Suppression of interleukin 1alpha and interleukin 1beta in human limbal epithelial cells cultured on the amniotic membrane stromal matrix
- PMID: 11264135
- PMCID: PMC1723909
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.85.4.444
Suppression of interleukin 1alpha and interleukin 1beta in human limbal epithelial cells cultured on the amniotic membrane stromal matrix
Abstract
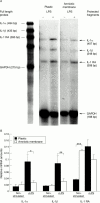
Aims: Amniotic membrane (AM) transplantation reduces inflammation in a variety of ocular surface disorders. The aim of this study was to determine if AM stroma suppresses the expression of the IL-1 gene family in cultured human corneal limbal epithelial cells.
Methods: Human corneal limbal epithelial cells were cultured from limbocorneal explants of donor eyes on plastic or on the AM stroma. Transcript expression of IL-1alpha, IL-1beta, IL-1 receptor antagonist (RA), and GAPDH was compared with or without addition of lipopolysaccharide to their serum-free media for 24 hours using RNAse protection assay (RPA). Their protein production in the supernatant was analysed by ELISA.
Results: Expression of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta transcripts and proteins was significantly reduced by cells cultured on the AM stromal matrix compared with plastic cultures whether lipopolysaccharide was added or not. Moreover, expression of IL-1 RA by cells cultured in the lipopolysaccharide-free medium was upregulated by AM stromal matrix. The ratio between IL-1 RA and IL-1alpha protein levels in AM cultures was higher than in plastic cultures.
Conclusions: AM stromal matrix markedly suppresses lipopolysaccharide induced upregulation of both IL-1alpha and IL-1beta. These data may explain in part the effect of AM transplantation in reducing ocular surface inflammation, underscoring the unique feature of the AM as a substrate for tissue engineering.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Doxycycline inhibition of interleukin-1 in the corneal epithelium.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000 Aug;41(9):2544-57. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000. PMID: 10937565
-
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) prevents apoptosis in ex vivo expansion of human limbal epithelial cells cultivated on human amniotic membrane.Stem Cells. 2006 Sep;24(9):2130-9. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2005-0590. Epub 2006 Jun 1. Stem Cells. 2006. PMID: 16741227
-
Role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in ex vivo expansion of human limbal epithelial cells cultured on human amniotic membrane.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Mar;46(3):808-15. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0370. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15728535
-
The role of NGF signaling in human limbal epithelium expanded by amniotic membrane culture.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002 Apr;43(4):987-94. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. PMID: 11923238
-
Ophthalmic applications of preserved human amniotic membrane: a review of current indications.Cell Tissue Bank. 2004;5(3):161-75. doi: 10.1023/B:CATB.0000046067.25057.0a. Cell Tissue Bank. 2004. PMID: 15509905 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Innovation of Tendon Tissue Engineering Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 14;21(18):6726. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186726. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32937830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Suture-free amniotic membrane transplantation].Ophthalmologe. 2013 Jul;110(7):675-80. doi: 10.1007/s00347-012-2742-5. Ophthalmologe. 2013. PMID: 23681176 German.
-
Synthetic bone substitute engineered with amniotic epithelial cells enhances bone regeneration after maxillary sinus augmentation.PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e63256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063256. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23696804 Free PMC article.
-
Amniotic membrane transplantation in the human eye.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011 Apr;108(14):243-8. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2011.0243. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011. PMID: 21547164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue remodeling after ocular surface reconstruction with denuded amniotic membrane.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 23;8(1):6400. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24694-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29686390 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
