Effects of anti-oestrogens and beta-estradiol on calcium uptake by cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 11264229
- PMCID: PMC1572683
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703924
Effects of anti-oestrogens and beta-estradiol on calcium uptake by cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
1. Tamoxifen and a group of structurally similar non-steroidal, triphenolic compounds inhibit the oestrogen receptor. In addition to this action, these anti-oestrogens are known to inhibit some types of plasma membrane ion channels and other proteins through mechanisms that do not appear to involve their interactions with the estrogen receptor but could be the result of their effect on membrane lipid structure or fluidity. 2. We studied the effects of beta-estradiol and three anti-oestrogens (tamoxifen, 4-hydroxytamoxifen and clomiphene) on Ca(2+) uptake into sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) vesicles isolated from canine cardiac ventricular tissue. 3. The antiestrogens all inhibit SR Ca(2+) uptake in a concentration-dependent manner (order of potency: tamoxifen > 4-hydroxytamoxifen > or = clomiphene). Although these compounds rapidly inhibit net Ca(2+) uptake they do not have a similar rapid effect on the ATPase activity of the SR Ca pump. beta-estradiol has no effect on Ca(2+) uptake nor does it alter the inhibitory action of tamoxifen on the SR. 4. The differences in the effects of beta-estradiol and the anti-oestrogens on cardiac SR Ca(2+) uptake do not correlate with differences in the ways in which these compounds have been reported to interact with membrane lipids. Our results are consistent, however, with direct effects on a membrane protein (possibly an SR Cl(-) or K(+) channel).
Figures
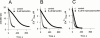




References
-
- BATRA S. Interaction of antiestrogens with binding sites for muscarinic cholinergic drugs and calcium channel blockers in cell membranes. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1990;26:310–312. - PubMed
-
- CHAMBERLAIN B.K., LEVITSKY D.O., FLEISCHER S. Isolation and characterization of canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum with improved Ca2+ transport properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1983;258:6602–6609. - PubMed
-
- CUSTÓDIO J.B.A., ALMEIDA L.M., MADEIRA V.M.C. The anticancer drug tamoxifen induces changes in the physical properties of model and native membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1993a;1150:123–129. - PubMed
-
- CUSTÓDIO J.B.A., ALMEIDA L.M., MADEIRA V.M.C. The active metabolite hydroxytamoxifen of the anticancer drug tamoxifen induces structural changes in membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1993b;1153:308–314. - PubMed
-
- CUSTÓDIO J.B.A., ALMEIDA L.M., MADEIRA V.M.C. The effect of the anticancer drugs tamoxifen and hydroxytamoxifen on the calcium pump of isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Toxicol. In Vitro. 1996;10:523–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

