Inhibition of aggregation of rabbit and human platelets induced by adrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine by KB-R7943, a Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange inhibitor
- PMID: 11264230
- PMCID: PMC1572684
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703928
Inhibition of aggregation of rabbit and human platelets induced by adrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine by KB-R7943, a Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange inhibitor
Abstract
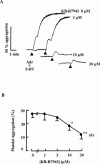
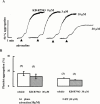
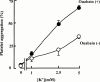
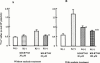
1. We investigated the effect of KB-R7943, a Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange inhibitor, on the aggregation response induced by adrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), alone or in combination in human and rabbit platelets in the presence or absence of ouabain. 2. KB-R7943 inhibited aggregation induced by the combination of adrenaline and 5-HT in a concentration-dependent manner. The IC(50) values of KB-R7943 were 4.2+/-2.0 or 3.0+/-0.7 microM with washed rabbit platelets with or without ouabain pretreatment, respectively. 3. In platelet-rich human plasma, the aggregation was biphasic. The IC(50) value of KB-R7943 was 17.2+/-4.4 microM for the first phase aggregation. 4. KB-R7943 did not inhibit the first phase of aggregation induced by adrenaline alone, or the monophasic aggregation induced by 5-HT alone. 5. The aggregation of rabbit platelets depended on the presence of K(+) in the medium, and K(+)-dependent and K(+)-independent Ca(2+) influx were observed in resting platelets. Ouabain treatment increased only the K(+)-dependent but not the K(+)-independent Ca(2+) influx. 6. KB-R7943 inhibited K(+)-dependent Ca(2+) influx with or without ouabain pretreatment, but not K(+)-independent Ca(2+) influx. 7. From these results, we conclude that KB-R7943 inhibits the adrenaline plus 5-HT induced aggregation of rabbit and human platelets by inhibiting K(+)-dependent Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange (NCKX). Our results suggest that NCKX plays an important role in platelet aggregation.
Figures
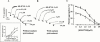

Similar articles
-
The novel Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange inhibitor KB-R7943 also blocks native and expressed neuronal nicotinic receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Aug;130(8):1893-902. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703519. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10952680 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a Na+/Ca2+ exchanger inhibitor on pulmonary vein electrical activity and ouabain-induced arrhythmogenicity.Cardiovasc Res. 2006 Jun 1;70(3):497-508. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.02.026. Epub 2006 Mar 3. Cardiovasc Res. 2006. PMID: 16574085
-
The plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+ exchange inhibitor KB-R7943 is also a potent inhibitor of the mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;151(5):647-54. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707260. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17471180 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and structural properties of the NCKX2 Na(+)-Ca (2+)/K (+) exchanger: a comparison with the NCX1 Na (+)/Ca (2+) exchanger.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;961:81-94. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4756-6_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224872 Review.
-
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors of platelets.Ciba Found Symp. 1975;35:287-307. doi: 10.1002/9780470720172.ch14. Ciba Found Symp. 1975. PMID: 776550 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Molecular and functional characterization of the human platelet Na(+) /Ca(2+) exchangers.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Feb;165(4):922-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01600.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21790537 Free PMC article.
-
Effect on ex vivo platelet aggregation and in vivo cyclic flow with Na+/H+ exchange inhibition: Gumina, NHE-1 inhibition and platelet aggregation.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2011 May;31(4):431-5. doi: 10.1007/s11239-010-0530-0. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2011. PMID: 21082215 Free PMC article.
-
A flagellar K(+)-dependent Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger keeps Ca(2+) low in sea urchin spermatozoa.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 May 14;99(10):6743-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.102186699. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12011436 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying presynaptic Ca2+ transient and vesicular glutamate release at a CNS nerve terminal during in vitro ischaemia.J Physiol. 2015 Jul 1;593(13):2793-806. doi: 10.1113/JP270060. Epub 2015 May 22. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25833340 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular sodium changes during the speract response and the acrosome reaction in sea urchin sperm.J Physiol. 2003 Jan 1;546(Pt 1):89-100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.030510. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12509481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BLAUSTEIN M.P., LEDERER W.J. Sodium/Calcium exchange: Its physiological implications. Physiol. Rev. 1999;47:763–854. - PubMed
-
- CERVETTO L., LAGNADO L., PERRY R.J., ROBINSON D.W., MCNAUGHTON P.A. Extrusion of calcium from rod outer segments is driven by both sodium and potassium gradients. Nature. 1989;337:740–743. - PubMed
-
- COLMAN R.W., WALSH P.N.Mechanisms of platelet aggregation Hemostasis and Thrombosis 1987Lippincott Co.: Philadelphia; 594–605.ed. Colman, R.W., Hirsh, J., Marder, V.J. & Salzman, E.W. pp
-
- HOLMSEN H.Platelet secretion Hemostasis and Thrombosis 1987Lippincott Co.: Philadelphia; 606–617.ed. Colman, R.W., Hirsh, J., Marder, V.J. & Salzman, E.W. pp
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

