Heterogeneous increases of cytoplasmic calcium: distinct effects on down-regulation of cell surface sodium channels and sodium channel subunit mRNA levels
- PMID: 11264239
- PMCID: PMC1572695
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703960
Heterogeneous increases of cytoplasmic calcium: distinct effects on down-regulation of cell surface sodium channels and sodium channel subunit mRNA levels
Abstract
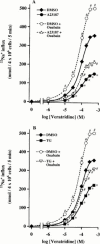
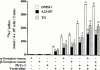
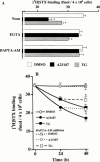
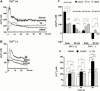
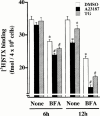
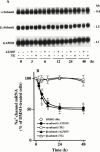
1. Long-term (> or = 12 h) treatment of cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells with A23187 (a Ca(2+) ionophore) or thapsigargin (TG) [an inhibitor of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA)] caused a time- and concentration-dependent reduction of cell surface [(3)H]-saxitoxin (STX) binding capacity, but did not change the K:(D:) value. In A23187- or TG-treated cells, veratridine-induced (22)Na(+) influx was reduced (with no change in veratridine EC(50) value) while it was enhanced by alpha-scorpion venom, beta-scorpion venom, or Ptychodiscus brevis toxin-3, like in nontreated cells. 2. The A23187- or TG-induced decrease of [(3)H]-STX binding was diminished by BAPTA-AM. EGTA also inhibited the decreasing effect of A23187. A23187 caused a rapid, monophasic and persistent increase in intracellular concentration of Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)](i)) to a greater extent than that observed with TG. 2,5-Di-(t-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone (DBHQ) (an inhibitor of SERCA) produced only a rapid monophasic increase in [Ca(2+)](i), without any effect on [(3)H]-STX binding. 3. Reduction in [(3)H]-STX binding capacity induced by A23187 or TG was attenuated by Gö6976 (an inhibitor of conventional protein kinase C) or calpastatin peptide (an inhibitor of calpain). When the internalization rate of cell surface Na(+) channels was measured in the presence of brefeldin A (an inhibitor of vesicular exit from the trans-Golgi network), A23187 or TG accelerated the reduction of [(3)H]-STX binding capacity. 4. Six hours treatment with A23187 lowered Na(+) channel alpha- and beta(1)-subunit mRNA levels, whereas TG had no effect. 5. These results suggest that elevation of [Ca(2+)](i) caused by A23187, TG or DBHQ exerted differential effects on down-regulation of cell surface functional Na(+) channels and Na(+) channel subunit mRNA levels.
Figures


References
-
- BRISMAR T. Abnormal Na-currents in diabetic rat nerve nodal membrane. Diabetic Med. 1993;10 Suppl. 2:110S–112S. - PubMed
-
- BRODIE C., BRODY M., SAMPSON S.R. Characterization of the relation between sodium channels and electrical activity in cultured rat skeletal myotubes: regulatory aspects. Brain Res. 1989;488:186–194. - PubMed
-
- CARAFOLI E., MOLINARI M. Calpain: a protease in search of a function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998;247:193–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

