Neurofilaments consist of distinct populations that can be distinguished by C-terminal phosphorylation, bundling, and axonal transport rate in growing axonal neurites
- PMID: 11264295
- PMCID: PMC6762414
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-07-02195.2001
Neurofilaments consist of distinct populations that can be distinguished by C-terminal phosphorylation, bundling, and axonal transport rate in growing axonal neurites
Abstract
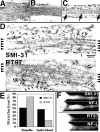
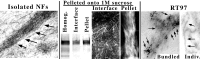
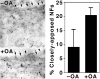
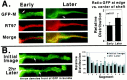
We examined the steady-state distribution and axonal transport of neurofilament (NF) subunits within growing axonal neurites of NB2a/d1 cells. Ultrastructural analyses demonstrated a longitudinally oriented "bundle" of closely apposed NFs that was surrounded by more widely spaced individual NFs. NF bundles were recovered during fractionation and could be isolated from individual NFs by sedimentation through sucrose. Immunoreactivity toward the restrictive C-terminal phospho-dependent antibody RT97 was significantly more prominent on bundled than on individual NFs. Microinjected biotinylated NF subunits, GFP-tagged NF subunits expressed after transfection, and radiolabeled endogenous subunits all associated with individual NFs before they associated with bundled NFs. Biotinylated and GFP-tagged NF subunits did not accumulate uniformly along bundled NFs; they initially appeared within the proximal portion of the NF bundle and only subsequently were observed along the entire length of bundled NFs. These findings demonstrate that axonal NFs are not homogeneous but, rather, consist of distinct populations. One of these is characterized by less extensive C-terminal phosphorylation and a relative lack of NF-NF interactions. The other is characterized by more extensive C-terminal NF phosphorylation and increased NF-NF interactions and either undergoes markedly slower axonal transport or does not transport and undergoes turnover via subunit and/or filament exchange with individual NFs. Inhibition of phosphatase activities increased NF-NF interactions within living cells. These findings collectively suggest that C-terminal phosphorylation and NF-NF interactions are responsible for slowing NF axonal transport.
Figures




References
-
- Anderton BH, Breinburg D, Downes MJ, Green PJ, Tomlinson BE, Ulrich J, Wood JN, Kahn J. Monoclonal antibodies show that neurofibrillary tangles and neurofilaments share antigenic determinants. Nature. 1982;298:84–86. - PubMed
-
- Baas PW, Brown A. Slow axonal transport: the polymer transport model. Trends Cell Biol. 1997;7:380–384. - PubMed
-
- Brady ST. Motor neurons and neurofilaments in sickness and health. Cell. 1993;73:1–3. - PubMed
-
- Brown AT. Visualization of single neurofilaments by immunofluo-rescence microscopy of splayed axonal cytoskeletons. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1997;38:133–145. - PubMed
-
- Brown AT. Contiguous phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated domains along axonal neurofilaments. J Cell Sci. 1998;111:455–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
