Formation and function of synapses with respect to Schwann cells at the end of motor nerve terminal branches on mature amphibian (Bufo marinus) muscle
- PMID: 11264312
- PMCID: PMC6762398
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-07-02380.2001
Formation and function of synapses with respect to Schwann cells at the end of motor nerve terminal branches on mature amphibian (Bufo marinus) muscle
Abstract
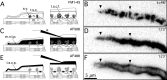
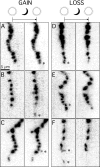
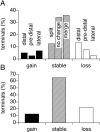
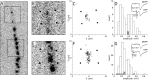
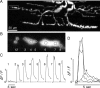
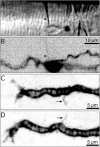
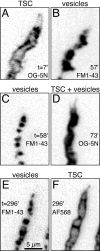
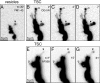
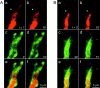
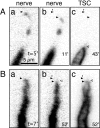
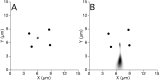
A study has been made of the formation and regression of synapses with respect to Schwann cells at the ends of motor nerve terminal branches in mature toad (Bufo marinus) muscle. Synapse formation and regression, as inferred from the appearance and loss of N-(3-triethylammoniumpropyl)-4-(4-(dibutylamino)styryl) pyridinium dibromide (FM1-43)-stained vesicle clusters, occurred at the ends of terminal branches over a 16 hr period. Multiple microelectrodes placed in an array about FM1-43 blobs at the ends of terminal branches detected the electrical signs of neurotransmitter being released onto receptors. Injection of a calcium indicator (Oregon Green 488 BAPTA-1) into the motor nerve with subsequent imaging of the calcium transients, in response to stimulation, often showed a reduced calcium influx in the ends of terminal branches. Injection of a fluorescent dye into motor nerves revealed the full extent of their terminal branches and growing processes. Injection of the terminal Schwann cells (TSCs) often revealed pseudopodial TSC processes up to 10-microm-long. Imaging of these TSC processes over minutes or hours showed that they were highly labile and capable of extending several micrometers in a few minutes. Injection of motor nerve terminals with a different dye to that injected into their TSCs revealed that terminal processes sometimes followed the TSC processes over a few hours. It is suggested that the ends of motor nerve terminals in vivo are in a constant state of remodeling through the formation and regression of processes, that TSC processes guide the remodeling, and that it can occur over a relatively short period of time.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmari SE, Buchanan J, Smith SJ. Assembly of presynaptic active zones from cytoplasmic transport packets. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:445–451. - PubMed
-
- Astrow SH, Qiang H, Ko CP. Perisynaptic Schwann cells at neuromuscular junctions revealed by a novel monoclonal antibody. J Neurocytol. 1998;27:667–681. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
