CNS region-specific oxytocin receptor expression: importance in regulation of anxiety and sex behavior
- PMID: 11264328
- PMCID: PMC6762393
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-07-02546.2001
CNS region-specific oxytocin receptor expression: importance in regulation of anxiety and sex behavior
Abstract
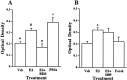
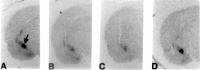
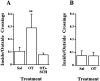
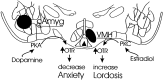
The oxytocin receptor (OTR) is differentially expressed in the CNS. Because there are multiple mechanisms by which the OTR can be transcriptionally induced, we hypothesized that differences in OTR expression may be explained by activation of distinct signal transduction pathways and may be critical for the control of anxiety and sex behaviors. To determine the regulation and functional significance of this expression, we infused female rats with modifiers of protein kinases before assaying for behavior and oxytocin receptor binding. In the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMH), estrogen-dependent induction of oxytocin receptors required protein kinase C activation, and oxytocin infused here promoted female sex behavior but had no effect on anxiety. In contrast, dopamine controlled tonic oxytocin receptor expression in the central nucleus of the amygdala (cAmyg) through activation of protein kinase A, and oxytocin infused here was anxiolytic but had no effect on female sex behavior. Therefore, we have identified brain region-specific regulation of the OTR in the VMH and cAmyg. Distinct signal transduction pathways regulating receptor expression and binding in each brain region may mediate in part the ability of oxytocin to exert these differential behavioral effects.
Figures



References
-
- Arletti R, Bertolini A. Oxytocin acts as an antidepressant in two animal models of depression. Life Sci. 1987;41:1725–1730. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL, Dorsa DM. Sex differences in and effects of estrogen on oxytocin receptor messenger ribonucleic acid expression in the ventromedial hypothalamus. Endocrinology. 1995a;136:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL, Dorsa DM. Regulation of oxytocin receptor messenger ribonucleic acid in the ventromedial hypothalamus by testosterone and its metabolites. Endocrinology. 1995b;136:5135–5138. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL, Dorsa DM. Cloning, novel promoter sequence, and estrogen regulation of a rat oxytocin receptor gene. Endocrinology. 1997;138:1151–1158. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL, Dorsa DM. NGF, cyclic AMP, and phorbol esters regulate oxytocin receptor gene transcription in SK-N-SH and MCF7 cells. Mol Brain Res. 1998;53:130–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
