Propagation of rat parvovirus in thymic lymphoma cell line C58(NT)d and subsequent appearance of a resistant cell clone after lytic infection
- PMID: 11264385
- PMCID: PMC114887
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.3965-3970.2001
Propagation of rat parvovirus in thymic lymphoma cell line C58(NT)d and subsequent appearance of a resistant cell clone after lytic infection
Abstract
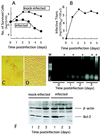
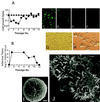
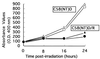
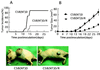
Rat parvovirus (RPV) is nonpathogenic in rats but causes persistent lymphocytotropic infection. We found that RPV was propagated in rat thymic lymphoma cell line C58(NT)D and induced apoptosis. Interestingly, a resistant subclone, C58(NT)D/R, from surviving cells after lytic infection had differentiated phenotypic modifications, such as increased cell adherence, resistance to apoptosis, and suppressed tumorigenicity.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

