TIF-IA, the factor mediating growth-dependent control of ribosomal RNA synthesis, is the mammalian homolog of yeast Rrn3p
- PMID: 11265758
- PMCID: PMC1084264
- DOI: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvd032
TIF-IA, the factor mediating growth-dependent control of ribosomal RNA synthesis, is the mammalian homolog of yeast Rrn3p
Abstract
Cells carefully modulate the rate of rRNA transcription in order to prevent an overinvestment in ribosome synthesis under less favorable nutritional conditions. In mammals, growth-dependent regulation of RNA polymerase I (Pol I) transcription is mediated by TIF-IA, an essential initiation factor that is active in extracts from growing but not starved or cycloheximide-treated mammalian cells. Here we report the molecular cloning and functional characterization of recombinant TIF-IA, which turns out to be the mammalian homolog of the yeast factor Rrn3p. We demonstrate that TIF-IA interacts with Pol I in the absence of template DNA, augments Pol I transcription in vivo and rescues transcription in extracts from growth-arrested cells in vitro.
Figures


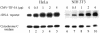

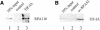

References
-
- Budde A. and Grummt, I. (1999) p53 represses ribosomal gene transcription. Oncogene, 18, 1119–1124. - PubMed
-
- Grummt I. (1999) Regulation of mammalian ribosomal gene transcription by RNA polymerase I. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol., 62, 109–154. - PubMed
-
- Mahajan P.B. and Thompson, E.A. (1990) Hormonal regulation of transcription of rDNA. Purification and characterization of the hormone-regulated transcription factor IC. J. Biol. Chem., 265, 16225–16233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

