Rab27a is required for regulated secretion in cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- PMID: 11266472
- PMCID: PMC2195783
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.152.4.825
Rab27a is required for regulated secretion in cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Abstract
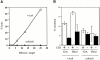
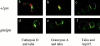
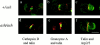
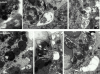
Rab27a activity is affected in several mouse models of human disease including Griscelli (ashen mice) and Hermansky-Pudlak (gunmetal mice) syndromes. A loss of function mutation occurs in the Rab27a gene in ashen (ash), whereas in gunmetal (gm) Rab27a dysfunction is secondary to a mutation in the alpha subunit of Rab geranylgeranyl transferase, an enzyme required for prenylation and activation of Rabs. We show here that Rab27a is normally expressed in cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), but absent in ashen homozygotes (ash/ash). Cytotoxicity and secretion assays show that ash/ash CTLs are unable to kill target cells or to secrete granzyme A and hexosaminidase. By immunofluorescence and electron microscopy, we show polarization but no membrane docking of ash/ash lytic granules at the immunological synapse. In gunmetal CTLs, we show underprenylation and redistribution of Rab27a to the cytosol, implying reduced activity. Gunmetal CTLs show a reduced ability to kill target cells but retain the ability to secrete hexosaminidase and granzyme A. However, only some of the granules polarize to the immunological synapse, and many remain dispersed around the periphery of the CTLs. These results demonstrate that Rab27a is required in a final secretory step and that other Rab proteins also affected in gunmetal are likely to be involved in polarization of the granules to the immunological synapse.
Figures




References
-
- Baetz K., Isaaz S., Griffiths G.M. Loss of cytotoxic T lymphocyte function in Chediak-Higashi syndrome arises from a secretory defect that prevents lytic granule exocytosis. J. Immunol. 1995;154:6122–6131. - PubMed
-
- Boissy R.E., Nordlund J.J. Molecular basis of congenital hypopigmentary disorders in humansa review. Pigment Cell Res. 1997;10:12–24. - PubMed
-
- Chen D., Guo J., Miki T., Tachibana M., Gahl W.A. Molecular cloning and characterization of rab27a and rab27b, novel human rab proteins shared by melanocytes and platelets. Biochem. Mol. Med. 1997;60:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Detter J.C., Zhang Q., Mules E.H., Novak E.K., Mishra V.S., Li W., McMurtrie E.B., Tchernev V.T., Wallace M.R., Seabra M.C., Swank R.T., Kingsmore S.F. Rab geranylgeranyl transferase alpha mutation in the gunmetal mouse reduces Rab prenylation and platelet synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:4144–4149. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fruth U., Prester M., Golecki J.R., Hengartner H., Simon H.G., Kramer M.D., Simon M.M. The T cell-specific serine proteinase TSP-1 is associated with cytoplasmic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 1987;17:613–621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

