Evidence for regulation of protein synthesis at the elongation step by CDK1/cyclin B phosphorylation
- PMID: 11266545
- PMCID: PMC31266
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.7.1453
Evidence for regulation of protein synthesis at the elongation step by CDK1/cyclin B phosphorylation
Abstract
Eukaryotic elongation factor 1 (eEF-1) contains the guanine nucleotide exchange factor eEF-1B that loads the G protein eEF-1A with GTP after each cycle of elongation during protein synthesis. Two features of eEF-1B have not yet been elucidated: (i) the presence of the unique valyl-tRNA synthetase; (ii) the significance of target sites for the cell cycle protein kinase CDK1/cyclin B. The roles of these two features were addressed by elongation measurements in vitro using cell-free extracts. A poly(GUA) template RNA was generated to support both poly(valine) and poly(serine) synthesis and poly(phenylalanine) synthesis was driven by a poly(uridylic acid) template. Elongation rates were in the order phenylalanine > valine > serine. Addition of CDK1/cyclin B decreased the elongation rate for valine whereas the rate for serine and phenylalanine elongation was increased. This effect was correlated with phosphorylation of the eEF-1delta and eEF-1gamma subunits of eEF-1B. Our results demonstrate specific regulation of elongation by CDK1/cyclin B phosphorylation.
Figures
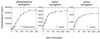


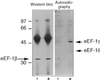
Similar articles
-
Regulation of elongation factor-2 by multisite phosphorylation.Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 15;213(2):689-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17809.x. Eur J Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8386634
-
Cyclin B2/cyclin-dependent kinase1 dissociation precedes CDK1 Thr-161 dephosphorylation upon M-phase promoting factor inactivation in Xenopus laevis cell-free extract.Int J Dev Biol. 2007;51(4):297-305. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.072292fc. Int J Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17554681
-
Insulin stimulation of phosphorylation of elongation factor 1 (eEF-1) enhances elongation activity.Eur J Biochem. 1998 Jan 15;251(1-2):201-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1998.2510201.x. Eur J Biochem. 1998. PMID: 9492285
-
Translational control during mitosis.Biochimie. 2005 Sep-Oct;87(9-10):805-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2005.04.014. Biochimie. 2005. PMID: 15951098 Review.
-
Phospho-p70S6K and cdc2/cdk1 as therapeutic targets for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009 Sep;13(9):1085-93. doi: 10.1517/14728220903103833. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009. PMID: 19614561 Review.
Cited by
-
Celiac anti-type 2 transglutaminase antibodies induce phosphoproteome modification in intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 31;8(12):e84403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084403. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24391952 Free PMC article.
-
CDK1 couples proliferation with protein synthesis.J Cell Biol. 2020 Mar 2;219(3):e201906147. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201906147. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32040547 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of a conserved CDK site converts a metazoan Elongation Factor 1Bbeta subunit into a replacement for yeast eEF1Balpha.Mol Genet Genomics. 2003 Sep;269(6):776-88. doi: 10.1007/s00438-003-0888-1. Epub 2003 Jul 30. Mol Genet Genomics. 2003. PMID: 12898219
-
Mapping the human translation elongation factor eEF1H complex using the yeast two-hybrid system.Biochem J. 2002 Aug 1;365(Pt 3):669-76. doi: 10.1042/BJ20011681. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 11985494 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila translational elongation factor-1gamma is modified in response to DOA kinase activity and is essential for cellular viability.Genetics. 2010 Jan;184(1):141-54. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.109553. Epub 2009 Oct 19. Genetics. 2010. PMID: 19841092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Day D.A. and Tuite,M.F. (1998) Post-transcriptional gene regulatory mechanisms in eukaryotes: an overview. J. Endocrinol., 157, 361–371. - PubMed
-
- Merrick W.C. and Hershey,J.W.B. (1996) The pathway and mechanism of eukaryotic protein synthesis. In Hershey,J.W.B., Mathews,M.B. and Sonenberg,N. (eds), Translational Control. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 31–69.
-
- Riis B., Rattam,S.I.S., Clark,B.F.C. and Merrick,W.C. (1990) Eukaryotic protein elongation factors. Trends Biochem. Sci., 15, 420–424. - PubMed
-
- Negrutskii B.S. and El’Skaya,A.V. (1998) Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1α: structure, expression, functions and possible role in aminoacyl-tRNA channeling. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol., 60, 47–78. - PubMed
-
- Hafezparast M. and Fisher,E. (1998) Wasted by an elongation factor. Trends Genet., 14, 215–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

