Cooperative binding of effectors by an allosteric ribozyme
- PMID: 11266567
- PMCID: PMC31269
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.7.1631
Cooperative binding of effectors by an allosteric ribozyme
Abstract
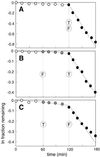
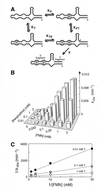
An allosteric ribozyme that requires two different effectors to induce catalysis was created using modular rational design. This ribozyme construct comprises five conjoined RNA modules that operate in concert as an obligate FMN- and theophylline-dependent molecular switch. When both effectors are present, this 'binary' RNA switch self-cleaves with a rate enhancement of approximately 300-fold over the rate observed in the absence of effectors. Kinetic and structural studies implicate a switching mechanism wherein FMN binding induces formation of the active ribozyme conformation. However, the binding site for FMN is rendered inactive unless theophylline first binds to its corresponding site and reorganizes the RNA structure. This example of cooperative binding between allosteric effectors reveals a level of structural and functional complexity for RNA that is similar to that observed with allosteric proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Competitive regulation of modular allosteric aptazymes by a small molecule and oligonucleotide effector.RNA. 2005 Oct;11(10):1514-20. doi: 10.1261/rna.2840805. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16199761 Free PMC article.
-
Design of allosteric hammerhead ribozymes activated by ligand-induced structure stabilization.Structure. 1999 Jul 15;7(7):783-91. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80102-6. Structure. 1999. PMID: 10425680
-
Expression mechanism of the allosteric interactions in a ribozyme catalysis.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 2000;(44):205-6. doi: 10.1093/nass/44.1.205. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 2000. PMID: 12903340
-
Molecular palaeontology: understanding catalytic mechanisms in the RNA world by excavating clues from a ribozyme three-dimensional structure.Biochem Soc Trans. 1996 Aug;24(3):604-8. doi: 10.1042/bst0240604. Biochem Soc Trans. 1996. PMID: 8878812 Review. No abstract available.
-
The many faces of the hairpin ribozyme: structural and functional variants of a small catalytic RNA.IUBMB Life. 2012 Jan;64(1):36-47. doi: 10.1002/iub.575. Epub 2011 Nov 30. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 22131309 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulating RNA structure and catalysis: lessons from small cleaving ribozymes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Dec;66(24):3937-50. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0124-1. Epub 2009 Aug 30. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19718544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modular, rule-based modeling for the design of eukaryotic synthetic gene circuits.BMC Syst Biol. 2013 May 27;7:42. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-7-42. BMC Syst Biol. 2013. PMID: 23705868 Free PMC article.
-
Rube Goldberg goes (ribo)nuclear? Molecular switches and sensors made from RNA.RNA. 2003 Apr;9(4):377-83. doi: 10.1261/rna.2200903. RNA. 2003. PMID: 12649489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensing complex regulatory networks by conformationally controlled hairpin ribozymes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jun 15;32(10):3212-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh643. Print 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004. PMID: 15199169 Free PMC article.
-
A self-cleaving DNA enzyme modified with amines, guanidines and imidazoles operates independently of divalent metal cations (M2+).Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(5):1638-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn1070. Epub 2009 Jan 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19153138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tang J. and Breaker,R.R. (1997) Rational design of allosteric ribozymes. Chem. Biol., 4, 453–459. - PubMed
-
- Soukup G.A. and Breaker,R.R. (1999) Design of allosteric hammerhead ribozymes activated by ligand-induced structure stabilization. Structure, 7, 783–791. - PubMed
-
- Breaker R.R. (1997) In vitro selection of catalytic polynucleotides. Chem. Rev., 97, 371–390. - PubMed
-
- Li Y. and Breaker,R.R. (1999) Deoxyribozymes: new players in the ancient game of biocatalysis. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 9, 315–323. - PubMed
-
- Wilson D.S. and Szostak,J.W. (1999) In vitro selection of functional nucleic acids. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 68, 611–647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

