Covalent intermediate trapped in 2-keto-3-deoxy-6- phosphogluconate (KDPG) aldolase structure at 1.95-A resolution
- PMID: 11274385
- PMCID: PMC31111
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.071380898
Covalent intermediate trapped in 2-keto-3-deoxy-6- phosphogluconate (KDPG) aldolase structure at 1.95-A resolution
Abstract
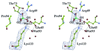
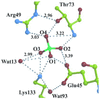
2-Keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate (KDPG) aldolase catalyzes the reversible cleavage of KDPG to pyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. The enzyme is a class I aldolase whose reaction mechanism involves formation of Schiff base intermediates between Lys-133 and a keto substrate. A covalent adduct was trapped by flash freezing KDPG aldolase crystals soaked with 10 mM pyruvate in acidic conditions at pH 4.6. Structure determination to 1.95-A resolution showed that pyruvate had undergone nucleophilic attack with Lys-133, forming a protonated carbinolamine intermediate, a functional Schiff base precursor, which was stabilized by hydrogen bonding with active site residues. Carbinolamine interaction with Glu-45 indicates general base catalysis of several rate steps. Stereospecific addition is ensured by aromatic interaction of Phe-135 with the pyruvate methyl group. In the native structure, Lys-133 donates all of its hydrogen bonds, indicating the presence of an epsilon-ammonium salt group. Nucleophilic activation is postulated to occur by proton transfer in the monoprotonated zwitterionic pair (Glu-45/Lys-133). Formation of the zwitterionic pair requires prior side chain rearrangement by protonated Lys-133 to displace a water molecule, hydrogen bonded to the zwitterionic residues.
Figures
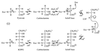

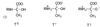

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

