Catalytic center of an archaeal type 2 ribonuclease H as revealed by X-ray crystallographic and mutational analyses
- PMID: 11274461
- PMCID: PMC2373963
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.48001
Catalytic center of an archaeal type 2 ribonuclease H as revealed by X-ray crystallographic and mutational analyses
Abstract
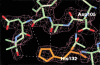
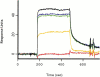
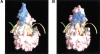
The catalytic center of an archaeal Type 2 RNase H has been identified by a combination of X-ray crystallographic and mutational analyses. The crystal structure of the Type 2 RNase H from Thermococcus kodakaraensis KOD1 has revealed that the N-terminal major domain adopts the RNase H fold, despite the poor sequence similarity to the Type 1 RNase H. Mutational analyses showed that the catalytic reaction requires four acidic residues, which are well conserved in the Type 1 RNase H and the members of the polynucleotidyl transferase family. Thus, the Type 1 and Type 2 RNases H seem to share a common catalytic mechanism, except for the requirement of histidine as a general base in the former enzyme. Combined with the results from deletion mutant analyses, the structure suggests that the C-terminal domain of the Type 2 RNase H is involved in the interaction with the DNA/RNA hybrid.
Figures
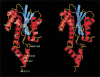

References
-
- Ariyoshi, M., Vassylyev, D.G., Iwasaki, H., Nakamura, H., Shinagawa, H., and Morikawa, K. 1994. Atomic structure of the RuvC resolvase: A Holliday junction-specific endonuclease from E. coli. Cell 82 209–220. - PubMed
-
- Brünger, A.T., Adams, P.D., Clore, G.M., DeLano, W.L., Gros, P., Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W., Jiang, J.S., Kuszewski, J., Nilges, M., Pannu, N.S., et al. 1998. Crystallography and NMR system (CNS): A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Cryst. D54 905–921. - PubMed
-
- Bujacz, G., Jaskolski, M., Alexandratos, J., and Wlodawer, A. 1995. High-resolution structure of the catalytic domain of avian sarcoma virus integrase. J. Mol. Biol. 253 333–346. - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4. 1994. The CCP4 suite: Programs for protein crystallography. Acta Cryst. D50 760–763. - PubMed
-
- Cowtan, K.D. 1994. "dm": An automated procedure for phase improvement by density modification. Joint CCP4 and ESF-EACBM Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 31 34– 38.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

