Involving patients in decisions regarding preventive health interventions using the analytic hierarchy process
- PMID: 11281910
- PMCID: PMC5081086
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1369-6513.2000.00075.x
Involving patients in decisions regarding preventive health interventions using the analytic hierarchy process
Abstract
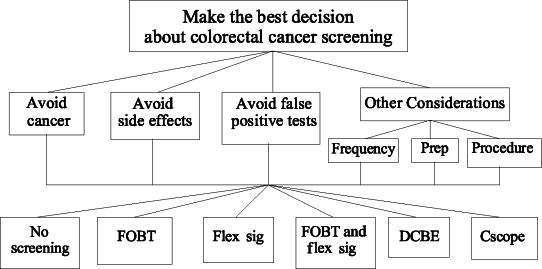
Practice guidelines that recommend active patient involvement in decisions about preventive health interventions are becoming increasingly common. These decisions frequently involve difficult trade-offs between competing risks and benefits that require easily accessible information about the expected outcomes, superb doctor-patient communication, and effective integration of objective outcome data with individual values and preferences. Successful implementation of recommendations for shared decision-making in preventive health care will require the development of efficient methods for making these complex decisions in busy practice settings. This article describes how the analytic hierarchy process, a multiple criteria decision-making method, could facilitate successful implementation of shared decision-making regarding preventive health care in clinical practice. The method is illustrated using recent guidelines for colorectal cancer screening for average risk patients issued by the American Gastroenterological Association.
Figures

References
-
- Winawer SJ, Fletcher RH, Miller L et al. Colorectal cancer screening: clinical guidelines and rationale. Gastroenterology, 1997; 112 : 594 642. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous . Guidelines for counselling post‐menopausal women about preventative hormone therapy. Annals of Internal Medicine, 1992; 117 : 1038 1041. - PubMed
-
- Coley CM, Barry MJ, Fleming C, Fahs MC, Mulley AG. Early detection of prostate cancer. Part II. Estimating the risks, benefits and costs. Annals of Internal Medicine, 1997; 126 : 468 479. - PubMed
-
- Pendergrass PW, DiGuiseppi C. Aspirin prophylaxis for primary prevention of myocardial infarction. In: DiGuiseppi C, Atkins D, Woolf S (eds) US Preventative Services Task Force Guide to Clinical Preventive Services (2nd edn.). Alexandria (VA): International Medical Publishing, 1996, 845–851.
-
- Forrow L, Wartman S, Brock D. Science, ethics and the making of clinical decisions. Implications for risk factor intervention. Journal of the American Medical Association, 1988; 259 : 3161 3167. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

