Biological activities and structural properties of the atypical bacteriocins mesenterocin 52b and leucocin b-ta33a
- PMID: 11282585
- PMCID: PMC92749
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.4.1418-1422.2001
Biological activities and structural properties of the atypical bacteriocins mesenterocin 52b and leucocin b-ta33a
Abstract
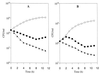
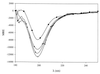
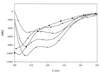
The antibacterial spectra and modes of action of synthetic peptides corresponding to mesenterocin 52B and leucocin B-TA33a greatly differ despite their high sequence homology. Circular dichroism experiments establish the capacity of each of these two peptides to partly fold into an amphiphilic helix that might be crucial for their adsorption at lipophilic-hydrophilic interfaces.
Figures

References
-
- Biet F, Berjeaud J M, Worobo R W, Cenatiempo Y, Frémaux C. Heterologous expression of the bacteriocin mesentericin Y105 using the dedicated transport system and the general secretion pathway. Microbiology. 1998;144:2845–2854. - PubMed
-
- Castedo A, Del Castillo J L, Suarez-Filloy M J, Rodriguez J R. Effect of temperature on the mixed micellar tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide-butanol system. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1997;196:148–156. - PubMed
-
- Chikindas M L, Garcia-Garcera M J, Driessen A J M, Ledeboer A M, Nissen-Meyer J, Nes I F, Abee T, Konings W N, Venema G. Pediocin PA-1, a bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0, forms hydrophilic pores in the cytoplasmic membrane of target cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993;59:3577–3584. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

