Degradation of phenanthrene and anthracene by cell suspensions of Mycobacterium sp. strain PYR-1
- PMID: 11282593
- PMCID: PMC92757
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.4.1476-1483.2001
Degradation of phenanthrene and anthracene by cell suspensions of Mycobacterium sp. strain PYR-1
Abstract
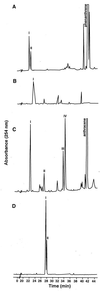
Cultures of Mycobacterium sp. strain PYR-1 were dosed with anthracene or phenanthrene and after 14 days of incubation had degraded 92 and 90% of the added anthracene and phenanthrene, respectively. The metabolites were extracted and identified by UV-visible light absorption, high-pressure liquid chromatography retention times, mass spectrometry, (1)H and (13)C nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry, and comparison to authentic compounds and literature data. Neutral-pH ethyl acetate extracts from anthracene-incubated cells showed four metabolites, identified as cis-1,2-dihydroxy-1,2-dihydroanthracene, 6,7-benzocoumarin, 1-methoxy-2-hydroxyanthracene, and 9,10-anthraquinone. A novel anthracene ring fission product was isolated from acidified culture media and was identified as 3-(2-carboxyvinyl)naphthalene-2-carboxylic acid. 6,7-Benzocoumarin was also found in that extract. When Mycobacterium sp. strain PYR-1 was grown in the presence of phenanthrene, three neutral metabolites were identified as cis- and trans-9,10-dihydroxy-9,10-dihydrophenanthrene and cis-3,4-dihydroxy-3,4-dihydrophenanthrene. Phenanthrene ring fission products, isolated from acid extracts, were identified as 2,2'-diphenic acid, 1-hydroxynaphthoic acid, and phthalic acid. The data point to the existence, next to already known routes for both gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, of alternative pathways that might be due to the presence of different dioxygenases or to a relaxed specificity of the same dioxygenase for initial attack on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Figures



References
-
- Akhtar N M, Boyd D R, Thompson M J, Koreeda M, Gibson D T, Mahadevan V, Jerina D M. Absolute stereochemistry of the dihydroanthracene-cis- and trans-1,2-diols produced from anthracene by mammals and bacteria. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans I. 1975;1:2506–2511. - PubMed
-
- Bouchez M, Blanchet D, Vandecastelle J P. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by pure strains and by defined strain associations: inhibition phenomena and cometabolism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1995;43:156–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

