Isolation and characterization of a slowly milk-coagulating variant of Lactobacillus helveticus deficient in purine biosynthesis
- PMID: 11282642
- PMCID: PMC92806
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.4.1846-1850.2001
Isolation and characterization of a slowly milk-coagulating variant of Lactobacillus helveticus deficient in purine biosynthesis
Abstract
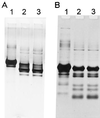
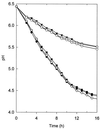
A slowly milk-coagulating variant (Fmc(-)) of Lactobacillus helveticus CRL 1062, designated S1, was isolated and characterized. Strain S1 possessed all the known essential components required to utilize casein as a nitrogen source, which include functional proteinase and peptidase activities as well as functional amino acid, di- and tripeptide, and oligopeptide transport systems. The amino acid requirements of strain S1 were similar to those of the parental strain. However, on a purine-free, chemically defined medium, the growth rate of the Fmc(-) strain was threefold lower than that of the wild-type strain. L. helveticus S1 was found to be defective in IMP dehydrogenase activity and therefore was deficient in the ability to synthesize XMP and GMP. This conclusion was further supported by the observation that the addition of guanine or xanthine to milk, a substrate poor in purine compounds, restored the Fmc(+) phenotype of L. helveticus S1.
Figures

References
-
- De Man J C, Rogosa M, Sharpe M E. A medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli. J Appl Bacteriol. 1960;23:130–135.
-
- De Rossi E, Brigidi P, Riccardi G, Milano A, Matteuzzi D. Preliminary studies on the correlation between the plasmid pLHJ1 and its proteolytic activity in Lactobacillus helveticus S 36.2. Physical mapping and molecular cloning of the plasmid in Escherichia coli. Microbiologica. 1989;12:273–276.
-
- Dickely F, Nilsson D, Hansen E B, Johansen E. Isolation of Lactococcus lactis nonsense suppressors and construction of a food-grade cloning vector. Mol Microbiol. 1995;15:839–847. - PubMed
-
- Elli M, Zink R, Rytz A, Reniero R, Morelli L. Iron requirement of Lactobacillus spp. in completely chemically defined growth media. J Appl Microbiol. 2000;88:695–703. - PubMed
-
- Exterkate F A. Differences in short peptide-substrate cleavage by two cell-envelope-located serine proteinases of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris are related to secondary binding specificity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990;33:401–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

