Deep desulfurization of extensively hydrodesulfurized middle distillate oil by Rhodococcus sp. strain ECRD-1
- PMID: 11282654
- PMCID: PMC92818
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.4.1949-1952.2001
Deep desulfurization of extensively hydrodesulfurized middle distillate oil by Rhodococcus sp. strain ECRD-1
Abstract
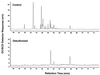
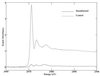
Dibenzothiophene (DBT), and in particular substituted DBTs, are resistant to hydrodesulfurization (HDS) and can persist in fuels even after aggressive HDS treatment. Treatment by Rhodococcus sp. strain ECRD-1 of a middle distillate oil whose sulfur content was virtually all substituted DBTs produced extensive desulfurization and a sulfur level of 56 ppm.
Figures
References
-
- Campbell I M. An orphaned child makes good—the story of US DoE/PETC's foray into fossil fuel biodesulphurization. Am Chem Soci Divi Petroleum Chem Preprints. 1993;38(2):275–278.
-
- Chang J H, Rhee S-K, Chang Y K, Chang H N. Desulfurization of diesel oils by a newly isolated dibenzothiophene-degrading Nocardia sp. strain CYKS2. Biotechnol Prog. 1998;14:851–855. - PubMed
-
- Gray K A, Pogrebinsky O S, Mrachko G T, Xi L, Monticello D J, Squires C H. Molecular mechanisms of biocatalytic desulfurization of fossil fuels. Nat Biotechnol. 1996;14:1705–1709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources