Lesson of the week: Acute hyponatraemia in children admitted to hospital: retrospective analysis of factors contributing to its development and resolution
- PMID: 11282868
- PMCID: PMC1119957
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.322.7289.780
Lesson of the week: Acute hyponatraemia in children admitted to hospital: retrospective analysis of factors contributing to its development and resolution
Figures
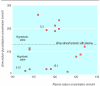

References
-
- Arieff AI. Hyponatremia, convulsions, respiratory arrest, and permanent brain damage after elective surgery in healthy women. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:1529–1535. - PubMed
-
- Halperin ML, Oh MS. The dysnatremias: hyponatremia and hypernatremia. In: Glassock RJ, editor. Current therapy in nephrology and hypertension. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby-Year Book; 1998. pp. 1–9.
-
- Darrow DC, Pratt EL. Fluid therapy. JAMA. 1950;143:365–373. - PubMed
-
- Halliday M, Segar W. The maintenance need for water in parenteral fluid therapy. Pediatrics. 1957;19:823–832. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
