PCR-based diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and real-time determination of clarithromycin resistance directly from human gastric biopsy samples
- PMID: 11283030
- PMCID: PMC87913
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.4.1217-1220.2001
PCR-based diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection and real-time determination of clarithromycin resistance directly from human gastric biopsy samples
Abstract
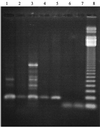
A novel PCR detection assay that amplifies the Helicobacter pylori-specific vacuolating cytotoxin gene (vacA) and thus enables rapid diagnosis of infection is described. Additionally, a real-time probe hybridization melting point analysis assay to detect all three mutations in the 23S rRNA gene associated with clarithromycin resistance was applied directly to antral gastric biopsy samples. Comparison with culture and an alternative PCR assay targeting the 16S rrn gene showed that the vacA assay was sensitive and specific when tested on biopsy samples from 121 patients. Clarithromycin susceptibilities could be determined in the majority (92.3%) of culture-positive gastric biopsy samples analyzed, four of which generated melting peaks indicative of clarithromycin resistance by either an A-->G or A-->C mutation. The presence of the mutations correlated with the clarithromycin disk diffusion sensitivities of matched cultures. This PCR-based system was simple to perform and could be completed in 3 to 4 h, thereby overcoming the delays associated with conventional culture methods for H. pylori identification and susceptibility testing.
Figures
References
-
- Atherton J C, Cao P, Peek R M, Jr, Tummuru M K, Blaser M J, Cover T L. Mosaicism in vacuolating cytotoxin alleles of Helicobacter pylori. Association of specific vacA types with cytotoxin production and peptic ulceration. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:17771–17777. - PubMed
-
- Cover T L. The vacuolating cytotoxin of Helicobacter pylori. Mol Microbiol. 1996;20:241–246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical