Evaluation of the NucliSens Basic Kit for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in genital tract specimens using nucleic acid sequence-based amplification of 16S rRNA
- PMID: 11283067
- PMCID: PMC87950
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.4.1429-1435.2001
Evaluation of the NucliSens Basic Kit for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in genital tract specimens using nucleic acid sequence-based amplification of 16S rRNA
Abstract
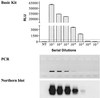
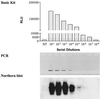
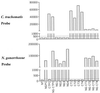
We evaluated a new RNA amplification and detection kit, the NucliSens Basic Kit (Organon Teknika), for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in genitourinary specimens. The Basic Kit provides an open platform for RNA amplification and detection and contains isolation reagents for nucleic acid extraction, nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) reagents (enzymes and buffers), and a generic ruthenium-labeled probe for electrochemiluminescent (ECL) detection of amplified product. Using freshly purified and titrated stocks of C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae and in vitro-generated RNA transcripts for sensitivity determinations, the Basic Kit detected 1 inclusion-forming unit of C. trachomatis, 1 CFU of N. gonorrhoeae, and 100 RNA molecules of 16S rRNA for both bacteria. The clinical performance of the Basic Kit was evaluated by testing a total of 250 specimens for N. gonorrhoeae by culture and NASBA and a total of 96 specimens for C. trachomatis by PCR and NASBA. The Basic Kit detected 139 of 142 N. gonorrhoeae culture-positive specimens and gave a negative result for 73 of 74 culture-negative specimens, for a sensitivity and specificity of 97.9 and 98.7%, respectively. For C. trachomatis, the Basic Kit detected 24 of 24 PCR-positive specimens and gave a negative result for 71 of 72 PCR-negative specimens, for a sensitivity and specificity of 100 and 98.6%, respectively. The Basic Kit also detected specimens containing both N. gonorrhoeae and C. trachomatis, using a multiplex NASBA assay using primers for both bacteria. The NucliSens Basic Kit offers a versatile platform for the development of sensitive RNA detection assays for sexually transmitted diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison between the LCx Probe system and the COBAS AMPLICOR system for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections in patients attending a clinic for treatment of sexually transmitted diseases in Amsterdam, The Netherlands.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Mar;39(3):829-35. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.3.829-835.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11230391 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex PCR for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Genitourinary specimens.J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Nov;33(11):3049-53. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.11.3049-3053.1995. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8576375 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in swab specimens by the Hybrid Capture II and PACE 2 nucleic acid probe tests.Sex Transm Dis. 1999 May;26(5):303-8. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199905000-00012. Sex Transm Dis. 1999. PMID: 10333286
-
Molecular diagnostics. The polymerase chain reaction and its use in the diagnosis of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Gac Med Mex. 1997;133 Suppl 1:133-7. Gac Med Mex. 1997. PMID: 9504115 Review.
-
Cervicovaginal microbiota in Chlamydia trachomatis and other preventable sexually transmitted infections of public health importance: a systematic umbrella review.New Microbiol. 2025 May;48(1):5-13. New Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40314676
Cited by
-
Prospective study of use of PCR amplification and sequencing of 16S ribosomal DNA from cerebrospinal fluid for diagnosis of bacterial meningitis in a clinical setting.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Feb;42(2):734-40. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.2.734-740.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 14766845 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide sequence-based multitarget identification.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Jul;41(7):3284-92. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.7.3284-3292.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12843076 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Chlamydia infection among women visiting a gynaecology outpatient department: evaluation of an in-house PCR assay for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2010 Sep 8;9:24. doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-9-24. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2010. PMID: 20822551 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of human papillomavirus infection in the oropharynx and urine among sexually active men: a comparative study of infection by papillomavirus and other organisms, including Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma spp., and Ureaplasma spp.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Jan 27;14:43. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-43. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24468054 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Directly Amplifying Nucleic Acids from Complex Samples.Biosensors (Basel). 2019 Sep 30;9(4):117. doi: 10.3390/bios9040117. Biosensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31574959 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anonymous. Global AIDS News—Newsletter of the World Health Organization Global Program on AIDS, no. 4. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1994. A new approach to STD control and AIDS prevention; pp. 13–15. - PubMed
-
- Carroll K C, Aldeen W E, Morrison M, Anderson R, Lee D, Mottice S. Evaluation of the Abbott LCx ligase chain reaction assay for detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in urine and genital swab specimens from a sexually transmitted disease clinic population. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:1630–1633. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommendations for the prevention and management of Chlamydia trachomatis infections. Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep. 1993;42:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

