16S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis distinguishes biotypes of Streptococcus bovis: Streptococcus bovis Biotype II/2 is a separate genospecies and the predominant clinical isolate in adult males
- PMID: 11283085
- PMCID: PMC87968
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.4.1549-1552.2001
16S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis distinguishes biotypes of Streptococcus bovis: Streptococcus bovis Biotype II/2 is a separate genospecies and the predominant clinical isolate in adult males
Abstract
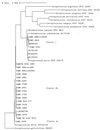
We characterized 22 human clinical strains of Streptococcus bovis by genotypic (16S rRNA gene sequence analysis [MicroSeq]; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, Calif.) and phenotypic (API 20 Strep and Rapid ID32 Strep systems (bioMerieux Vitek, Hazelton, Mo.) methods. The strains, isolated from blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and urine, formed two distinct 16S ribosomal DNA sequence clusters. Three strains which were associated with endocarditis urinary tract infection (UTI), and sepsis clustered with the S. bovis type strain ATCC 33317 (cluster 1); other closely related type strains were S. equinus and S. infantarius. Nineteen strains clustered at a distance of about 2.5% dissimilarity to the S. bovis type strain (cluster 2) and were associated with central nervous system (CNS) disease in addition to endocarditis, UTI, and sepsis. All strains were distinct from S. gallolyticus. Within cluster 2, a single strain grouped with ATCC strain 43143 (cluster 2a) and may be phenotypically distinct. All the other strains formed a second subgroup (cluster 2b) that was biochemically similar to S. bovis biotype II/2 (mannitol negative and beta galactosidase, alpha galactosidase, beta glucuronidase, and trehalose positive). The API 20 Strep system identified isolates of cluster 2b as S. bovis biotype II/2, those of cluster 1 as S. bovis biotype II/1, and that of cluster 2a as S. bovis biotype I. There was an excellent correlation of biotype and genotype: S. bovis biotype II/2 isolates form a separate genospecies distinct from the S. bovis, S. gallolyticus, and S. infantarius type strains and are the most common isolates in adult males.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adherence characteristics of endocarditis-derived Streptococcus gallolyticus ssp. gallolyticus (Streptococcus bovis biotype I) isolates to host extracellular matrix proteins.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008 Dec;289(1):104-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01378.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2008. PMID: 19054100
-
Taxonomic dissection of the Streptococcus bovis group by analysis of manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase gene (sodA) sequences: reclassification of 'Streptococcus infantarius subsp. coli' as Streptococcus lutetiensis sp. nov. and of Streptococcus bovis biotype 11.2 as Streptococcus pasteurianus sp. nov.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002 Jul;52(Pt 4):1247-1255. doi: 10.1099/00207713-52-4-1247. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12148636
-
Reappraisal of the taxonomy of the Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex and related species: description of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus subsp. nov., S. gallolyticus subsp. macedonicus subsp. nov. and S. gallolyticus subsp. pasteurianus subsp. nov.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2003 May;53(Pt 3):631-645. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02361-0. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12807180
-
Genomics, evolution, and molecular epidemiology of the Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex (SBSEC).Infect Genet Evol. 2015 Jul;33:419-36. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2014.09.017. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Infect Genet Evol. 2015. PMID: 25233845 Review.
-
Neonatal sepsis caused by Streptococcus bovis variant (biotype II/2): report of a case and review.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Jul;41(7):3433-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.7.3433-3435.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12843113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Update on the Streptococcus bovis Group: Classification, Identification, and Disease Associations.J Clin Microbiol. 2016 Jul;54(7):1694-1699. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02977-15. Epub 2016 Feb 24. J Clin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26912760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of clinically relevant viridans group streptococci by sequence analysis of the 16S-23S ribosomal DNA spacer region.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Jun;42(6):2651-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.6.2651-2657.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15184447 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Streptococcus bovis endocarditis and its differences with Streptococcus viridans endocarditis.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008 Apr;27(4):285-91. doi: 10.1007/s10096-007-0441-y. Epub 2008 Jan 9. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18183440
-
Association of tannase-producing Staphylococcus lugdunensis with colon cancer and characterization of a novel tannase gene.J Gastroenterol. 2007 May;42(5):346-51. doi: 10.1007/s00535-007-2012-5. Epub 2007 May 25. J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17530358
-
High prevalence of inducible erythromycin resistance among Streptococcus bovis isolates in Taiwan.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Dec;45(12):3362-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.12.3362-3365.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11709309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bovet A, Grimont F, Collins M D, Benaoudia F, Devine C, Regnault B, Grimont P A. Streptococcus infantarius sp. nov. related to Streptococcus bovis and Streptococcus equinus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;418:393–395. - PubMed
-
- Cohen L, Dunbar S, Clarridge J E., III Streptococcus bovis infection of the central nervous system: report of two cases and review. Clin Infect Disease. 1997;25:819–823. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous