Protein kinase C isoform-dependent modulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels during reoxygenation in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes
- PMID: 11283232
- PMCID: PMC2278517
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0165g.x
Protein kinase C isoform-dependent modulation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels during reoxygenation in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes
Abstract
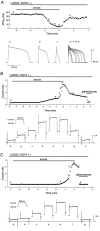
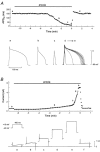
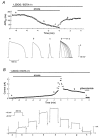
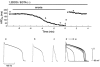
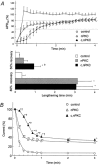
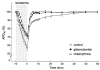
ATP-sensitive K+ (KATP) channels activated by glucose-free anoxia close immediately upon reoxygenation in single guinea-pig ventricular myocytes, while KATP channels open persistently during reperfusion in coronary-perfused guinea-pig ventricular myocardium. To investigate the reasons behind this discrepancy, we investigated whether protein kinase C (PKC) modulates the opening of KATP channels during anoxia-reoxygenation and ischaemia-reperfusion. Exposure of guinea-pig ventricular cells to glucose-free anoxia shortened the action potential duration at 90% repolarisation (APD90) and evoked the glibenclamide-sensitive robust outward current (IK,ATP). Subsequent reoxygenation caused an immediate prolongation of APD90 and a decrease in IK,ATP within approximately 20 s. When the novel (Ca2+-independent) PKC was activated by applying 1,2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycerol (1,2DOG, 20 M) with EGTA (20 mM) in the pipette, the APD90 restored gradually after reoxygenation and the extent of recovery was appoximately 80% of the pre-anoxic value. Moreover, IK,ATP decreased slowly and remained opened for up to approximately 4 min after reoxygenation. These results suggest persistent opening of KATP channels during reoxygenation. The persistent activation of KATP channels was augmented when both novel and conventional (Ca2+-dependent) isoforms of PKC were activated by applying 1,2DOG without EGTA in the pipette. In coronary-perfused right ventricular myocardium, APD90 remained shortened for up to approximately 30 min of reperfusion. The gradual restoration of APD90 after ischaemia-reperfusion was facilitated by the KATP channel blocker glibenclamide and by the potent PKC inhibitor chelerythrine. Our results provide the first evidence that PKC activation contributes to the persistent opening of KATP channels during reoxygenation and reperfusion. We also conclude that both novel and conventional PKC isoforms co-operatively modulate the opening of KATP channels during the early phase of reoxygenation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of anoxic preconditioning on ATP-sensitive potassium channels in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes.Pflugers Arch. 2000 Apr;439(6):808-13. doi: 10.1007/s004249900200. Pflugers Arch. 2000. PMID: 10784356
-
Anoxia-induced activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in guinea pig ventricular cells and its modulation by glycolysis.Cardiovasc Res. 1997 Aug;35(2):273-82. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(97)00092-8. Cardiovasc Res. 1997. PMID: 9349390
-
JTV-519, a novel cardioprotective agent, improves the contractile recovery after ischaemia-reperfusion in coronary perfused guinea-pig ventricular muscles.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Jun;130(4):767-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703373. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10864882 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological functions of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in myocardial ischemia.Jpn Heart J. 1997 May;38(3):297-315. doi: 10.1536/ihj.38.297. Jpn Heart J. 1997. PMID: 9290566 Review.
-
The impact of ATP-sensitive K+ channel subtype selectivity of insulin secretagogues for the coronary vasculature and the myocardium.Diabetes. 2004 Dec;53 Suppl 3:S156-64. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.suppl_3.s156. Diabetes. 2004. PMID: 15561904 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of cardiac ATP-sensitive potassium channel surface expression by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 18;288(3):1568-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.429548. Epub 2012 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23223335 Free PMC article.
-
KATP Channels in the Cardiovascular System.Physiol Rev. 2016 Jan;96(1):177-252. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00003.2015. Physiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 26660852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel subunit, Kir6.2, by a Ca2+-dependent protein kinase C.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6196-207. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.243923. Epub 2011 Dec 29. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22207763 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac and vascular KATP channels in rats are activated by endogenous epoxyeicosatrienoic acids through different mechanisms.J Physiol. 2006 Sep 1;575(Pt 2):627-44. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.113985. Epub 2006 Jun 22. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16793897 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal KATP channels as a reservoir after myocardial ischemia: a role for SUR2 subunits.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Jan;300(1):H262-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00857.2010. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20971764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black SC, Fagbemi SO, Chi L, Friedrichs GS, Lucchesi BR. Phorbol ester-induced ventricular fibrillation in the Langendorff-perfused rabbit heart: antagonism by staurosporine and glibenclamide. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 1993;25:1427–1438. - PubMed
-
- Clement PJ, IV, Kunjilwar K, Gonzalez G, Schwanstercher M, Panten U, Aguilar-Bryan L, Bryan J. Association and stoichiometry of KATP channel subunit. Neuron. 1997;18:827–838. - PubMed
-
- Garlid KD, Paucek P, Yarov-Yarovoy V, Murray HM, Darbenzo RB, D'Alonzo AJ, Smith MA, Grover GJ. Cardioprotective effect of diazoxide and its interaction with mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channels: possible mechanism of cardioprotection. Circulation Research. 1997;81:1072–1082. - PubMed
-
- Grover GJ, D'Alonzo AJ, Parham CS, Darbenzio RB. Cardioprotection with the KATP opener cromakalim is not correlated with ischaemic myocardial action potential duration. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 1995;26:145–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

